Anemia Treatment in India
Anemia is a common blood condition marked by the body's insufficient production of healthy red blood cells. It causes tiredness, weakness, pale skin, and shortness of breath. Many people around the world – adults, children, and pregnant women – face anemia. The good news is that India offers high-quality anemia care at a much lower cost than in the US, UK, Canada, or Australia. The cost of anemia treatment in India ranges from USD 5,000 to USD 40,000, and thousands of international patients travel to India for treatment.
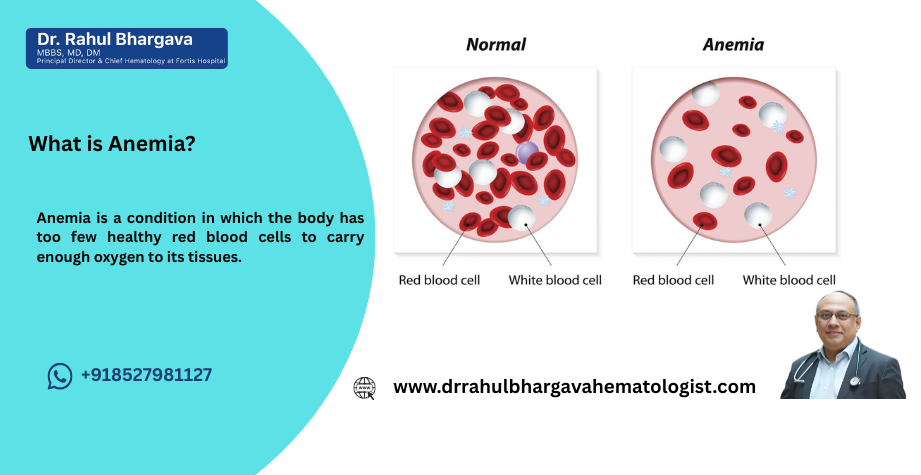
What is Anemia?
Anemia means your blood has too little hemoglobin or too few red cells. Hemoglobin is the part of red blood cells that carries oxygen. When there is not enough of it, your body tissues get less oxygen. Common symptoms are tiredness, feeling weak or dizzy, and pale skin. Some patients also experience feelings of coldness or palpitations in the heart. Anemia can be mild or severe. Mild anemia might make you feel tired, while severe anemia can make you feel very weak or even make the heart beat faster.
Major Types of Anemia
There are several major types of anemia. They have different causes and treatments. The main kinds are:
Iron-Deficiency Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is one of the most common types worldwide. It happens when your body doesn't have enough iron to make hemoglobin. Common causes include poor diet (not enough iron-rich foods), heavy menstrual bleeding in women, stomach ulcers, or other blood loss. It's also common during pregnancy or in growing children, as they require more iron.
- Symptoms: Patients often experience fatigue, weakness, or lightheadedness. They might have pale skin and gums or nails that are thin or spoon-shaped. You might get winded easily doing light exercise. Simple things, like climbing stairs, can feel challenging.
- Diagnosis: Doctors do a simple blood test called a Complete Blood Count (CBC). It shows low hemoglobin and small red cells. They also check iron levels (serum iron and ferritin tests). These tests are quick and inexpensive in India (often just a few dollars).
- Treatment: The treatment is usually straightforward.
- If it's mild, doctors may prescribe iron supplements (pills or syrup). These replace the missing iron. Common pills (like ferrous sulfate) cost very little in India – often just a few rupees per tablet (a month's supply might be only USD 5–10). Patients are also advised to consume iron-rich foods, such as spinach, beans, and red meat, if possible. Vitamin C (found in citrus fruits) is advised with iron because it helps the body absorb iron better.
- If anemia is more severe or if someone can't take pills, intravenous (IV) iron infusions are an option. In India, an IV iron infusion (a drip of iron solution administered at a clinic) typically costs around INR 6,000–10,000 (approximately USD 80–130) per dose. This is usually much cheaper than in Western countries. After a few infusions, iron levels go up, and the person feels better.
Thalassemia
Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder. In this disorder, the body makes an abnormal form of hemoglobin. Depending on the type, it can cause mild to severe anemia. India has a significant number of people with thalassemia, especially in some communities. If both parents carry the thalassemia gene, their child can have beta-thalassemia major, a severe form of the condition.
- Symptoms: Individuals with thalassemia major often develop anemia in early childhood. They may grow slowly and exhibit symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, pale skin, and an enlarged spleen (a small organ located under the ribs). Sometimes, bones in the face grow oddly to make more marrow. If untreated, children can be very sick.
- Diagnosis: Thalassemia is diagnosed by blood tests. A CBC will show anemia. Then, tests such as Hemoglobin Electrophoresis or High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) are performed. These tests cost more (maybe USD 30–40 in India), but they find the exact type of hemoglobin issue.
- Treatment: Patients with severe thalassemia usually need regular blood transfusions. This means getting a unit of donor blood every few weeks. Each transfusion can raise hemoglobin for a short time. Because of these transfusions, iron can build up in the body over time, so patients also need iron chelation therapy. This is a medicine that removes extra iron.
- Blood Transfusions: In India, a typical transfusion session (1–2 units) costs around INR 13,000 (approximately USD 160), including hospital fees. For comparison, in the US, one unit of blood might cost USD 300–USD 500 or more. Many thalassemia patients need transfusions every 3–4 weeks, so in a year, the blood alone might cost a few thousand dollars in India.
- Iron Chelation: Doctors administer medications such as deferasirox or deferoxamine to remove excess iron from the body. In India, generic versions are available. A year's supply of chelation can cost around INR 150,000–INR 250,000 (USD 2,000–USD 3,300) – still much lower than in the West, where it can be USD 15,000–USD 20,000 a year.
- Other Supplements: Doctors also give folic acid (a B vitamin) and ensure good nutrition. Folic acid pills cost only a few hundred rupees a month in India.
- Bone Marrow/Stem Cell Transplant: It is a potential cure for thalassemia. If a suitable donor (often a sibling) is found, a transplant can replace the bone marrow. In India, a bone marrow transplant for thalassemia typically costs around INR 25–35 lakh (approximately USD 30,000–USD 45,000), depending on the city and hospital. In contrast, the same transplant in the USA or UK often costs well over USD 150,000. Because of this significant price difference, many international families consider India for a transplant.
Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia is another inherited condition. It mainly affects people with ancestry from Africa, the Middle East, or South Asia. In sickle cell disease, the RBCs become stiff and crescent-shaped ("sickle"-shaped) instead of round. These abnormal RBCs can clog small blood vessels, causing pain crises and organ damage over time.
- Symptoms: Symptoms often start in childhood. Common problems are episodes of severe pain (called sickle crises), especially in the back, chest, or limbs. Patients also have chronic anemia symptoms (tiredness, paleness). They may be more susceptible to infections because sickle cells can damage the spleen.
- Diagnosis: A simple blood test can detect sickle cell trait or disease. Newborns are often screened in many countries. In India, hemoglobin electrophoresis or HPLC tests are used.
- Treatment: Many treatments focus on managing pain and preventing crises:
- Hydroxyurea: A pill that reduces pain crises and helps make red cells less "sticky." In India, a vial of generic hydroxyurea costs approximately INR 600 (USD 7), whereas branded versions abroad may cost hundreds of dollars.
- Blood Transfusions: Some patients receive periodic transfusions to reduce their sickle cell counts. Cost per transfusion is similar to thalassemia (INR 7,000–21,000).
- Pain Management: When crises happen, hospitals give pain medicines (like opioids) and IV fluids. In India, even a short hospital stay for pain control is much cheaper than in Western countries.
- Curative Transplant: Like thalassemia, the only cure is a bone marrow transplant. India offers sickle cell transplants at lower prices. Reports suggest a transplant for sickle cell might start at around USD 22,000 in India. Abroad, it can be over USD 100,000.
Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious condition. It means the bone marrow is not making enough blood cells – red cells, white cells, and platelets all can be very low. Aplastic anemia can develop at any age. Causes include certain infections, specific medications, or autoimmune conditions (where the body attacks its own marrow). Sometimes, it's inherited.
- Symptoms: Because all blood cells are low, symptoms include extreme fatigue (from low red cells), infections and fevers (from low white cells), and easy bruising or bleeding (from low platelets). Skin rashes and dizziness are also common. It can make people very sick quickly.
- Diagnosis: Doctors confirm this with a bone marrow biopsy, which reveals an empty marrow (containing very few blood-forming cells). This test costs around USD 100–USD 150 in India.
- Treatment:
- Immunosuppressive Therapy (IST): If there is no matching donor for transplant or the patient is older, doctors often use medicines to try to "restart" the marrow. The standard treatment consists of ATG (anti-thymocyte globulin) administered intravenously for several days, followed by cyclosporine pills for several months. In India, a full course of IST costs roughly USD 8,000–USD 12,000 (including drugs and hospital stays). In the US, this therapy alone could cost over USD 50,000.
- Bone Marrow Transplant: For suitable young patients with a matching sibling donor, a transplant is the best option. In India, an allogeneic transplant costs about INR 20–30 lakh (USD 25,000–USD 35,000). This compares to USD 400,000–USD 500,000 in the USA. Many top hospitals in India perform these transplants with good success rates.
- Supportive Care: Since blood counts are low, patients often need transfusions of blood cells and platelets. In India, transfusions are significantly less expensive. Also, doctors give antibiotics to prevent infections. If transfusions cause iron buildup, chelation medicines (such as deferasirox) are used.
Anemia Treatment Options and Costs in India
Whether you're suffering from iron deficiency, thalassemia, sickle cell disease, or aplastic anemia, India offers world-class treatment at a fraction of the cost. Here is a breakdown of the primary treatment categories and their associated costs in India.
Iron Deficiency Anemia Treatment Cost in India
Iron deficiency is the most common type of anemia. Fortunately, it is also the easiest to treat. In India, a one-month supply of iron tablets costs between USD 1 and USD 3, compared to USD 10 to USD 20 in the US or UK. For patients who can't tolerate oral tablets, IV iron therapy is available. Each session of iron infusion in India ranges from USD 80 to USD 130, while the same can cost USD 500 to USD 1,000 in Western countries.
If the anemia is severe, a blood transfusion may be needed. In India, each unit of packed red blood cells (PRBC) ranges from USD 90 to USD 270, including screening and transfusion fees. The same treatment abroad can easily cost more than USD 1,000 per unit.
Thalassemia Treatment Cost in India
Thalassemia is a genetic form of anemia that requires lifelong care. Patients often need monthly blood transfusions. The cost per transfusion in India ranges from USD 90 to USD 270, whereas in countries like the US, it can be as high as USD 1,000 or more.
Over time, iron accumulates in the body, so patients often require iron chelation therapy to manage this accumulation. In India, oral chelation medicines cost between USD 2,000 and USD 3,300 per year. This is significantly lower than in the West, where costs can rise from USD 15,000 to USD 20,000 annually.
For some patients, a bone marrow transplant offers a potential cure. In India, this life-saving procedure costs between USD 25,000 and USD 45,000. In comparison, the same treatment may cost between USD 150,000 and USD 500,000 in countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom.
Sickle Cell Anemia Treatment Cost in India
Sickle cell anemia is another inherited form of anemia that is common in some populations. India offers excellent treatment options at low prices. The primary drug used is hydroxyurea. A one-month supply in India costs USD 7 to USD 15, compared to USD 300 to USD 800 in Western markets.
When needed, patients may also require blood transfusions or even bone marrow transplants. Again, these treatments follow the same price pattern – up to 70% less expensive in India than in the West.
Aplastic Anemia Treatment Cost in India
Treatment of aplastic anemia involves immunosuppressive therapy or a bone marrow transplant. Immunosuppressive therapy, which includes ATG and cyclosporine, typically costs between USD 8,000 and USD 12,000 in India. In the US or UK, this can cost between USD 50,000 and USD 80,000.
Bone marrow transplants for aplastic anemia are also available in India, with costs ranging from USD 25,000 to USD 45,000 for international patients. This is a fraction of the price in most Western nations.
Vitamin B12 and Folate Deficiency Anemia
These are also common and very affordable to treat in India. A month's supply of vitamin B12 or folic acid supplements costs less than USD 5, while in the US or UK, it can cost USD 10 to USD 30. Injections are also available at a very low cost.
Diagnostic and Consultation Costs
Before starting treatment, patients must undergo blood tests and consult with a healthcare professional. In India, a complete anemia workup—including CBC, iron levels, vitamin B12, and folate—costs around USD 20 to USD 50. Specialist consultation with a hematologist ranges from USD 20 to USD 40 in most hospitals. These same services can cost between USD 100 and USD 300 or more in Western countries.
Factors Affecting Anemia Treatment Costs in India
The total cost of anemia treatment in India can vary depending on several key factors:
- Type and Severity of Anemia: Simple iron-deficiency anemia is cheaper to treat than thalassemia or aplastic anemia. Chronic or genetic anemias need long-term treatment, increasing overall cost.
- City or Location Treatment in metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Bangalore may cost slightly more than in smaller towns. However, these cities offer advanced technology and better infrastructure for international patients.
- Type of Treatment: Oral medications like iron tablets or folic acid are inexpensive. Advanced treatments, such as bone marrow transplants, iron chelation therapy, or dialysis, can significantly increase costs.
- Inpatient vs. Outpatient: Outpatient treatments, such as oral medications or injections, are generally less expensive than inpatient treatments. Inpatient procedures like transfusions or transplants include bed charges, nursing, and meals.
- Duration of Treatment: Some treatments last for a few weeks, others for a lifetime (like in thalassemia). Annual costs for long-term conditions, such as sickle cell or chronic kidney disease (CKD)- related anemia, can accumulate over time.
Success Rate of Anemia Treatments in India
India has a strong track record in treating all types of anemia. Success rates depend on the stage of diagnosis, type of anemia, and overall health of the patient.
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: Over 95% recovery with proper treatment. Most patients feel better within a few weeks.
- Thalassemia: Supportive care (transfusions + chelation) gives patients a near-normal life expectancy. Bone marrow transplant (BMT) offers a 75–90% cure rate in younger patients with a matched donor.
- Sickle Cell Disease: With medication and regular care, many patients live full lives. BMT success rates are around 80–90% in well-matched cases.
- Aplastic Anemia: Immunosuppressive therapy (IST) helps 60–70% of patients recover. Bone marrow transplant success rates range between 70% and 90%, especially in children.
Why Choose India for Anemia Treatment?
Patients from countries like SAARC, GCC, Fiji, Nigeria, Kenya, Bangladesh, and the UAE often travel to India for anemia care. The reasons are simple:
- High-Quality Care: Top Indian hospitals have modern equipment (MRI, labs, transplant suites) and follow international treatment protocols. Many doctors publish research and train globally.
- Expertise: India treats thousands of anemia patients each year. There are centers of excellence for thalassemia and bone marrow transplants. Doctors here are experienced with all types of anemia.
- Lower Costs: As shown above, nearly every aspect of care is much cheaper in India – medications, tests, procedures, and hospital stays. Many clinics in India advertise anemia treatment costs that are 10–20% of the US prices. It can translate to saving thousands of dollars in the event of a serious illness.
- No Long Waits: Unlike some countries with lengthy public health wait times, private Indian hospitals typically see patients promptly. Once you arrive, tests and treatment can begin in a matter of days.
- Language and Comfort: English is widely used in medical settings, so communication is easy for Western patients. Hospitals often cater to international norms (private rooms, international food options, etc.).
- Support Services: Dedicated patient coordinators, visa assistance, lodging arrangements, and even shopping and holiday tours make it a patient-friendly experience.
- Cultural Experience: Some patients appreciate the chance to visit India's cultural sites, meet people, and return home with new experiences.
Planning Your Anemia Treatment in India
For international patients, planning is key. Here are essential things to know:
Visa and Travel
- Medical Visa: Foreign patients seeking medical treatment in India must apply for a medical visa. Many nationalities can do this online (e-Medical Visa). You need a letter from an Indian hospital inviting you for treatment. The visa fee is modest (often USD 50–USD 100) and usually allows multiple entries for up to 6 months. You may extend it if treatment takes longer. Two family members can get an attendant visa linked to yours.
- Hospital Invitation: Once you contact a hospital in India, they will often assist with obtaining a visa letter. They might also help with filling out forms.
- Flights: Major Indian cities, such as Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Bangalore, have international airports with flights from around the world.
- Arrival: Hospitals usually offer airport pick-up. You'll be taken to your hotel or the hospital if you're being admitted.
Choosing a Hospital and Doctor
- Accreditation: Look for hospitals with international certification (such as JCI or NABH). These meet global care standards. Many big private hospitals in India have these—for example, Fortis Memorial Research Institute in Gurgaon.
- Specialists: Seek out hematology or hemato-oncology departments. Indian doctors, such as Dr. Rahul Bhargava, are experienced with diseases like thalassemia and sickle cell.
- International Services: Good hospitals have an "International Patients" office. They assist foreign patients with logistics, including scheduling tests, arranging interpreters, handling billing, and navigating the hospital. Use these services – it makes everything easier.
- Language: English is widely spoken by doctors and staff. Patient documents and reports will be in English. If you need translators (for Arabic, Russian, etc.), ask the hospital; many have staff or volunteers.
- Location: Big metro cities offer more hospitals and specialists. Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai, and Hyderabad are among the most common choices. Each has large tertiary hospitals.
Interpreter and Support Services
- Translators: English is usually enough, but if needed, some hospitals provide translation services for other languages. Verify in advance.
- Medical Travel Agencies: Several agencies in India specialize in medical tourism. They coordinate appointments, visas, travel, and even tour packages. They may charge fees but can simplify arrangements.
- Local Help: Hospitals often assign a coordinator or "case manager" to international patients. This person guides you through admission, tests, treatment, and discharge.
- Emergency: Good hospitals have 24/7 labs and emergency units. In the event of an urgent situation (such as severe bleeding or infection), care is available around the clock.
Accommodation and Recovery
- Hotels and Guest Houses: There are lodging options to fit every budget. Near large hospitals, you'll find guest houses (INR 1,000–3,000 per night, USD 15–USD 40) or service apartments. Hotels range from budget (USD 30/night) to luxury (USD 100).
- Hospital Guest Rooms: Some hospitals have in-house "guest rooms" for patients' families. These are more affordable and located inside the hospital campus.
- Meals: Indian hospital meals are generally vegetarian by default, with non-vegetarian options available upon request. International patients can also order external food (delivery from local restaurants).
- Tourism: Many patients add a short holiday after treatment. India boasts historic sites, stunning beaches (such as those in Goa), and a diverse array of cultural experiences. If your health allows, sightseeing can be a part of recovery. (However, avoid strenuous activity until fully healed.)
Interpreter, Transport, and Other Needs
- Language: As mentioned, English is generally accepted by most hospitals. For Hindi or local languages, ask for an interpreter.
- Transport: Hospitals can arrange local transport. You can also use prepaid taxis or ride-share apps (Uber, Ola). Private drivers can be hired at reasonable daily rates.
- Medical Equipment: If you need special equipment (such as a wheelchair or medication), many hospitals stock or can source it at a low cost.
- Pharmacy: Every hospital has a pharmacy with all needed medicines. Prices are low. You might even buy a year's supply of chronic medication to take home, usually cheaper than abroad.
- SIM Card and Wi-Fi: On arrival, you can buy a local SIM card (requires your passport). Most hotels and hospitals have free Wi-Fi for guests.
For international patients with anemia, India offers a compelling combination of world-class care and cost-effective treatment. Whether your anemia is due to genetics (thalassemia or sickle cell), iron deficiency, marrow failure, or chronic illness, India's hospitals have the expertise to treat it effectively. The cost of anemia treatment in India is usually a fraction of that in Western countries. Patients pay less for doctor fees, hospital stays, medications, and life-saving procedures, such as bone marrow transplants.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, India is considered very safe for medical care. The country has many world-class hospitals with international accreditations, experienced doctors, and English-speaking staff. These hospitals follow global standards and are well-equipped to treat all types of anemia, including complex cases.
Your stay depends on the type of anemia and treatment you require. For simple iron-deficiency anemia, a stay of 3 to 7 days is usually enough. If you're coming for blood transfusions or thalassemia management, plan for a stay of 1 to 2 weeks. For advanced procedures like bone marrow or kidney transplants, you may need to stay between 4 and 8 weeks to allow for recovery and follow-up.
To travel to India for treatment, you will need a valid passport, a medical visa, and your recent medical records. The hospital you choose will usually provide a visa invitation letter to help with the application process. Some hospitals even offer visa assistance and fast-tracking services for international patients.
This depends on your insurance provider and country of residence. Some global health insurance policies reimburse treatment costs in India if the hospital is accredited and the treatment is pre-approved. It's best to check with your insurance company before making travel arrangements.
Yes, most Indian hospitals offer ongoing support for international patients. After you return home, you can stay in touch with your doctor through video calls, emails, or phone consultations. They can also review lab reports and help you adjust medications, ensuring a smooth and safe recovery.
Bone marrow transplant is currently the only permanent cure for these conditions. However, not all patients need a transplant. Many live healthy lives with regular blood transfusions, iron chelation, and medication. Your doctor in India will guide you on whether a transplant is the best option for your case.
Yes, Indian hospitals deliver treatment outcomes that are often equal to those in the West. Doctors in top Indian hospitals are trained internationally, and the medical technology used is up to global standards. Plus, the success rates for procedures like bone marrow transplants and anemia management are very high—often at a much lower cost.