Aplastic Anemia Treatment in India
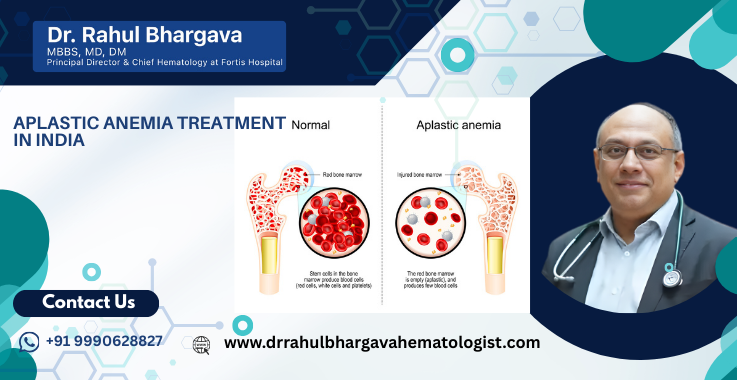
Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious blood disorder in which the bone marrow fails to produce enough red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This condition leads to chronic fatigue, frequent infections, and an increased risk of bleeding. Aplastic anemia can be either acquired, resulting from autoimmune reactions, diseases, or certain medications, or inherited, as seen in conditions such as Fanconi anemia.
The cost of immunosuppressive therapy in India typically ranges from $8,000 to $12,000 USD. In comparison, a bone marrow transplant may cost around $25,000 to $35,000 USD, compared to $250,000 or more in countries like the USA. Supportive care, including blood transfusions and post-treatment monitoring, can add $1,500 to $3,000 USD annually, making India a top destination for cost-effective, world-class treatment for aplastic anemia.
What Is Aplastic Anemia?
Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious blood disorder in which the bone marrow fails to produce enough new blood cells. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue inside bones that makes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In aplastic anemia, this production slows down or stops altogether, leading to a condition called pancytopenia — a shortage of all three types of blood cells.
How many Types of Aplastic Anemia?
1. Acquired Aplastic Anemia (Most Common)
This type develops later in life and is not inherited. It occurs when something damages the bone marrow, resulting in reduced or stopped production of blood cells.
Common Causes:
- Autoimmune response (the body attacks its marrow)
- Viral infections (e.g., Hepatitis, EBV, HIV)
- Medications (e.g., chemotherapy, antibiotics like chloramphenicol)
- Toxins and chemicals (e.g., benzene, pesticides)
- Radiation or cancer therapy
- Unknown (Idiopathic) – No clear cause in ~70% of cases
Age group: Most commonly affects adolescents and adults
Treatments: Immunosuppressive therapy or bone marrow transplant
2. Inherited (Congenital) Aplastic Anemia
This type is caused by genetic mutations passed from parents to children. It is usually diagnosed in early childhood and may be associated with physical abnormalities or other syndromes.
Major Subtypes:
- Fanconi Anemia (FA) – Most common inherited type
- Associated with bone malformations, short stature, and skin pigmentation
- Dyskeratosis Congenita
- Affects nails, skin, and causes marrow failure
- Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome
- Diamond-Blackfan Anemia (rare, often classified separately)
Age group: Infants and young children
Treatments: Bone marrow transplant is often required early in life
Summary Table
| Type | Cause | Common Age Group | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acquired Aplastic Anemia | Environmental/Autoimmune | Adolescents & Adults | IST, Bone Marrow Transplant |
| Inherited Aplastic Anemia | Genetic Mutations | Children | Bone Marrow Transplant, Supportive |
Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia :
Common Symptoms :
- Extreme Fatigue and Weakness: Due to a lack of red blood cells.
- Shortness of Breath: Often related to anemia.
- Frequent or Prolonged Infections: Due to a deficiency of white blood cells.
- Easy Bruising or Bleeding: Because of a low platelet count.
- Skin Rashes: Often related to low platelet counts.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness Resulting from anemia.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Diagnostic Workup Includes:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Shows pancytopenia
- Reticulocyte count: Low
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: Hypocellular marrow with no infiltration or fibrosis
- Serologic tests: Rule out viral causes (EBV, Hepatitis, HIV)
- Flow cytometry: To rule out PNH (Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria)
- Genetic tests: If inherited causes are suspected
Severity Classification
| Type | ANC (/µL) | Platelets (/µL) | Reticulocyte Count (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-severe | >500 | >20,000 | >1% |
| Severe | <500 | <20,000 | <1% |
| Very Severe | <200 | <20,000 | <1% |
First-Line Treatments
A. Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT)
- Indication: Preferred for patients <40 years with a matched sibling donor
- Conditioning regimen: Cyclophosphamide + ATG ± Fludarabine
- Outcome: 75–90% survival with sibling donor transplant
Cost in India for international patients:
- $25,000 – $35,000
B. Immunosuppressive Therapy (IST)
- Indicated for:
- Patients >40 years
- No matched sibling donor
- Moderate to severe disease
- Standard Protocol (Horse ATG + Cyclosporine):
- ATG (Antithymocyte Globulin): 40 mg/kg/day × 4 days
- Cyclosporine: 5 mg/kg/day (oral), continued for 6–12 months
- ± Eltrombopag (TPO receptor agonist) to improve outcomes
- Response Rate: ~60–70% within 3–6 months
💰 Cost in India (IST full course):
$8,000 – $12,000
Supportive Management
- Blood transfusions: PRBCs and platelets as needed
- Infection control: Prophylactic antibiotics/antifungals
- Growth factors: G-CSF may be used selectively
- Iron chelation therapy: For transfusion-related iron overload
Second-Line and Salvage Therapy
If no response to first-line IST in 6 months:
- Alternative donor BMT (unrelated matched donor or haploidentical)
- Eltrombopag alone or in combination
- Alemtuzumab (Campath) – experimental settings
- Enrollment in clinical trials, if available
Monitoring Schedule
| Parameter | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| CBC | Weekly initially | Monitor recovery |
| Renal/Liver Function | Monthly | Cyclosporine toxicity |
| Ferritin | Every 3 months | Iron overload |
| Bone Marrow Biopsy | 6 months | Response evaluation |
| Cyclosporine Levels | As indicated | Maintain therapeutic range |
Aplastic Anemia Treatment Cost Comparison (India vs Turkey vs USA)
| Treatment Type | India (USD) | Turkey (USD) | USA (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Workup (CBC, Bone Marrow, Viral Panel) | $300 – $700 | $1,000 – $2,000 | $5,000 – $10,000 |
| Immunosuppressive Therapy (ATG + Cyclosporine) | $8,000 – $12,000 | $15,000 – $20,000 | $50,000 – $70,000 |
| Eltrombopag (3–6 months course) | $2,500 – $4,000 | $5,000 – $7,000 | $15,000 – $20,000 |
| Supportive Blood Transfusions (annual) | $1,500 – $3,000 | $4,000 – $6,000 | $20,000 – $30,000 |
| Iron Chelation Therapy (if required annually) | $1,000 – $2,000 | $3,000 – $5,000 | $15,000 – $25,000 |
| Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant (Allo-BMT) | $25,000 – $35,000 | $40,000 – $60,000 | $400,000 – $500,000 |
| HLA Typing + Donor Matching | $600 – $900 | $1,000 – $1,500 | $5,000 – $10,000 |
| Hospital Stay (BMT/IST, 3–4 weeks) | $1,500 – $3,000 | $4,000 – $6,000 | $20,000 – $50,000 |
| Infection Prophylaxis + Growth Factors (monthly) | $200 – $400 | $500 – $800 | $2,000 – $4,000 |
| Post-Treatment Monitoring (6–12 months) | $500 – $1,200 | $1,500 – $3,000 | $10,000 – $20,000 |
Recovery Period of Aplastic Anemia
The recovery period for aplastic anemia varies depending on the severity of the condition, the type of treatment received, and the individual patient’s response. Recovery doesn’t happen overnight—it is a gradual process that can range from several months to over a year.
1. Recovery After Immunosuppressive Therapy (IST)
Medications: Antithymocyte globulin (ATG) + Cyclosporine ± Eltrombopag
Timeline:
- Initial response: Within 3 to 6 months
- Full hematologic recovery: Up to 12 months
- Some patients may require maintenance cyclosporine for 1–2 years
Monitoring:
- Weekly CBC during the first 3 months
- Monthly blood tests thereafter
- Liver/kidney function and cyclosporine levels every few weeks
Notes:
- About 60–70% of patients respond to IST
- Some patients may relapse or develop late clonal disorders like PNH or MDS
2. Recovery After Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT)
Best candidates: Young patients with matched sibling donors
Timeline:
- Engraftment (initial recovery): 14–28 days post-transplant
- Immune system recovery: 3–6 months for partial, up to 12 months for full immune recovery
- Overall full recovery: Typically 6–12 months, sometimes longer
Monitoring:
- Daily labs during hospital stay (first 30–40 days)
- Weekly to monthly follow-ups for 6–12 months
- Lifelong yearly monitoring for complications or relapse
Notes:
- BMT has a cure rate of up to 90% in ideal conditions
- Graft vs. host disease (GvHD), infections, and organ toxicity are key risks
3. Recovery with Supportive Care Only
For patients not undergoing definitive treatment:
- Symptoms managed with transfusions
- No curative recovery unless spontaneous remission occurs (rare)
- The risk of iron overload, infections, and bleeding remains long-term
Summary Table: Aplastic Anemia Recovery Timeline
| Treatment | Response Starts | Full Recovery Time | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immunosuppressive Therapy | 3–6 months | 6–12 months | ~60–70% |
| Bone Marrow Transplant | 2–4 weeks (engraft) | 6–12 months | ~75–90% (matched donor) |
| Supportive Care | Symptom-based | No curative recovery | Palliative management |
Frequently Asked Questions
Aplastic anemia is a condition where the bone marrow stops producing enough new blood cells, affecting red cells, white cells, and platelets, which can lead to fatigue, infections, and bleeding.
It can be caused by autoimmune disorders, exposure to toxic chemicals, viral infections, certain medications, or inherited genetic disorders. In many cases, the cause remains unknown (idiopathic).
Common treatments include blood transfusions, immunosuppressive therapy, medications, and bone marrow transplant (BMT), depending on the severity and patient condition.
Diagnosis involves a complete blood count (CBC), bone marrow biopsy, peripheral blood smear, reticulocyte count, and additional tests to rule out infections or autoimmune causes.
Treatment costs vary: Blood transfusions: ₹7,000 – ₹21,000 per session BMT: ₹18,00,000 – ₹37,00,000 Immunosuppressive therapy: ₹1,50,000 – ₹3,70,000 per month Medications: ₹35,000 – ₹1,50,000 per month Diagnostic tests: ₹1,500 – ₹1,10,000