Autologous Stem Cell Transplant in India
Autologous stem cell transplant is a powerful treatment option for patients battling blood cancers like multiple myeloma, lymphoma, and certain autoimmune diseases. In India, this life-saving procedure is not only advanced and accessible but also remarkably affordable. The cost of an autologous stem cell transplant in India typically ranges between $20,000 and $30,000, which is significantly lower than in the United States or Europe, where the same procedure can cost upwards of $100,000. With world-class hospitals, internationally trained hematologists, and patient-centred services, India is a preferred destination for international patients seeking safe and cost-effective transplant care.
What Is an Autologous Stem Cell Transplant?
An autologous stem cell or bone marrow transplant is a specialized procedure in which a patient's own healthy stem cells are collected, preserved, and then reintroduced into their body after intensive treatment. It is most commonly used to treat multiple myeloma, Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and some autoimmune or neurological disorders.
The process starts with the extraction of stem cells from the patient's bloodstream or bone marrow. These cells are frozen and stored while the patient undergoes high-dose chemotherapy or radiation to eliminate cancerous cells. Once this is complete, the stored stem cells are reinfused to help regenerate the bone marrow and restore the immune system.
Unlike allogeneic transplants, which use cells from a donor, autologous transplants pose no risk of rejection or graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) because the stem cells are derived from the patient's own body. This makes it a safer option for many patients, especially when donor matching is difficult or when minimizing complications is a priority.
Autologous transplants are considered a standard-of-care treatment in India for eligible patients and are performed in specialized bone marrow transplant units that adhere to rigorous infection control protocols.
Who Needs an Autologous Stem Cell Transplant?
An autologous stem cell transplant is typically recommended for patients who require intensive treatment for certain cancers or immune-related conditions but are still strong enough to undergo the procedure. Autologous transplant allows doctors to administer high-dose chemotherapy or radiation that would otherwise damage the bone marrow, knowing that healthy stem cells will later restore it.
The most common conditions for which autologous stem cell transplantation is indicated are:
- Multiple Myeloma: Patients with multiple myeloma are among the most frequent recipients of autologous transplants. The procedure is often used as a first-line consolidation treatment after initial chemotherapy, significantly improving remission duration and overall survival.
- Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL): For patients with aggressive or relapsed forms of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma, high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous transplant offers a chance for long-term disease control or cure.
- Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Autologous transplant is often used for Hodgkin's lymphoma that does not respond to standard chemotherapy or recurs after initial remission. It can be curative in many such cases.
- Germ Cell Tumors: In rare cases, autologous transplant is used in patients with relapsed or refractory testicular cancer or ovarian germ cell tumors, especially when they fail to respond to conventional therapies.
- Autoimmune Diseases: In select cases of severe autoimmune disorders such as systemic sclerosis or multiple sclerosis, autologous transplant may be used as an immune "reset" therapy to halt disease progression.
- Certain Neurological or Metabolic Conditions: Emerging research supports autologous transplantation in a few inherited disorders, though these are less common and typically done in clinical trial settings.
What are the Eligibility Criteria for Autologous Stem Cell Transplant?
Not every patient is immediately eligible for an autologous stem cell transplant. Indian hospitals adhere to strict protocols to ensure safety and optimal outcomes. The following factors are evaluated before proceeding:
- Type of Disease: Conditions like multiple myeloma, Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and certain solid tumors are ideal candidates.
- Disease Status: The patient's disease should be in partial or complete remission after initial chemotherapy.
- Organ Function: Proper heart, liver, kidney, and lung function is essential for tolerating and recovering from high-dose chemotherapy.
- Age and Fitness Level: While there's no fixed age cut-off, patients should be in good general health. Even elderly patients may qualify if fit.
- Infection-Free Status: Patients should be free of active infections, HIV, or uncontrolled comorbidities.
- Psychological Readiness and Support: Mental preparedness and a strong caregiver system are critical for post-transplant recovery and adherence.
What is the Difference Between Autologous and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants?
Autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplants are two primary types of bone marrow transplants, differing significantly in terms of source, risk, and suitability.
- In an autologous transplant, the patient's own healthy stem cells are harvested before intensive chemotherapy and then re-infused. This method is primarily used in the treatment of multiple myeloma, lymphoma, and certain autoimmune disorders. The most significant advantage is that there is no risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) since the cells come from the patient's own body.
- In contrast, an allogeneic transplant uses stem cells from a donor, either a matched sibling, an unrelated donor, or a haploidentical (half-matched) family member. This type is often used for leukemias, aplastic anemia, and genetic blood disorders. Allogeneic transplants carry a higher risk of adverse effects such as GVHD but may offer a graft-versus-cancer effect, where donor cells help eliminate any residual cancer.
Choosing between the two depends on the disease, stage, and the patient's overall health. Autologous transplants are generally safer, with faster recovery and fewer complications.
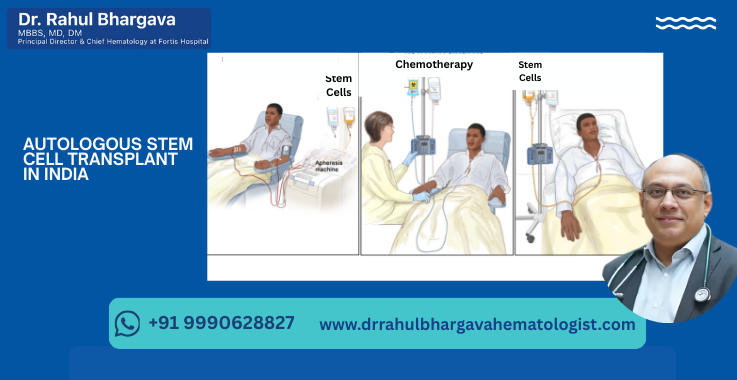
Step-by-Step Process of Autologous Stem Cell Transplant in India
Autologous stem cell transplantation in India follows a structured and internationally approved protocol designed to ensure maximum safety, effectiveness, and patient comfort. The entire process (from evaluation to recovery) usually spans over 4 to 6 weeks of hospitalization, followed by outpatient follow-ups. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide to how the procedure is carried out in top Indian hospitals:
- Pre-Transplant Evaluation: Before the procedure begins, patients undergo thorough medical assessments to determine transplant eligibility. It includes complete blood work, imaging (such as PET/CT scans or MRI), liver and kidney function tests, infection screening, and a bone marrow biopsy (if necessary). These evaluations help ensure the patient is physically ready for high-dose therapy and the stem cell transplant.
- Mobilization and Stem Cell Collection: To collect stem cells, doctors stimulate the bone marrow to release them into the bloodstream. It is done using medications like G-CSF (granulocyte-colony stimulating factor), often combined with chemotherapy. Once stem cells are mobilized:
- Blood is drawn through a process called apheresis, usually over 1–2 days
- The stem cells are separated and collected while the rest of the blood is returned to the patient
- The collected cells are then frozen and preserved using cryopreservation until needed
- Conditioning Regimen (High-Dose Chemotherapy): The patient is admitted to a specialized transplant unit and given high-dose chemotherapy. This intense regimen destroys any remaining cancer cells but also wipes out the bone marrow. The most common drugs used include melphalan, BEAM, or other tailored combinations depending on the disease.
- Stem Cell Infusion (Day 0): A few days after chemotherapy, the preserved stem cells are thawed and infused into the patient via a central venous line. This process is similar to a blood transfusion and usually takes a few hours. It is a critical milestone in the transplant journey, referred to as "Day 0."
- Engraftment: The infused stem cells travel to the marrow and begin regenerating blood cells, a process known as engraftment, which typically occurs within 10 to 14 days after infusion. During this phase:
- Patients are closely monitored for infections, bleeding, or organ dysfunction
- Daily blood tests are conducted to track white cells, red cells, and platelets
- Supportive medications and transfusions are provided as needed
- The patient stays in a HEPA-filtered room to reduce infection risk
- Discharge and Follow-Up: Once engraftment is confirmed and the patient is stable, they are discharged with detailed instructions on hygiene, diet, and medications. Regular follow-ups are scheduled to monitor recovery, manage side effects, and adjust medications.
What is the Cost of an Autologous Stem Cell Transplant in India?
The average cost of an autologous stem cell transplant in India ranges from $20,000 to $30,000, depending on factors such as the type of disease, the hospital, location, and the patient's health status. However, it is approximately 70% to 80% cheaper than the same procedure in countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, or Germany.
For comparison:
|
Country |
Average Cost (in USD) |
|
India |
20,000 – 30,000 |
|
United States |
120,000 – 200,000 |
|
United Kingdom |
100,000 – 180,000 |
|
Germany |
110,000 – 170,000 |
|
Turkey |
40,000 – 60,000 |
|
Thailand |
50,000 – 70,000 |
Even when international travel and lodging are factored in, India remains the most cost-effective choice for stem cell transplants.
What Does the Cost Typically Include?
Most Indian hospitals offer package-based pricing for international patients, which may include:
- Pre-transplant investigations and diagnostics
- Stem cell mobilization and collection
- Cryopreservation and storage
- High-dose chemotherapy
- Stem cell infusion
- Hospital stay (typically 25 to 30 days)
- Post-transplant supportive care
- Medications during hospital stay
What are the Factors Affecting the Cost of Autologous Stem Cell Transplants in India?
While India offers a cost-effective solution for patients requiring autologous stem cell transplants, the final expense can vary based on several key factors.
- Underlying Disease and Stage of Treatment: The cost may differ depending on the disorder being treated. For instance, patients with multiple myeloma may have different chemotherapy regimens and monitoring needs compared to those with lymphoma or autoimmune diseases. Advanced or relapsed cases often require additional interventions, increasing the total cost.
- Hospital and City Chosen for Treatment: Premium hospitals in metro cities like Delhi and Chennai may charge slightly higher due to advanced infrastructure and international accreditations. However, these facilities often offer world-class care, infection-controlled BMT units, and English-speaking staff, which are especially beneficial for international patients.
- Pre-Transplant Evaluation and Additional Testing: Patients with comorbidities may need extended evaluations, specialist consultations, or cardiac, liver, and kidney assessments before the transplant. These additional tests can add to the baseline package cost.
- Duration of Hospital Stay and Recovery Time: A standard autologous transplant hospitalization lasts around 3-4 weeks. However, if a patient develops complications like infections or delayed engraftment, they may require ICU care or an extended stay, which can significantly raise the overall cost.
- Cost of Medications and Supportive Care: Certain post-transplant medications, including antibiotics, growth factors, and antifungals, can be expensive. The requirement for blood transfusions, nutritional support, or isolation care may also impact the final bill.
- Room Category and Amenities: Indian hospitals offer a range of room options, from shared wards to deluxe suites. International patients typically choose private or semi-private rooms, which are more comfortable but come at a higher cost.
- Currency Exchange Rates and Payment Mode: Fluctuating exchange rates can affect the cost for patients from countries with volatile currencies. Some hospitals also provide installment payment options or discounts for upfront payment.
- Post-Discharge Accommodation and Follow-Up Costs: Although not included in the hospital package, patients should also budget for hotel or guesthouse stays, transportation, nutritional supplements, and post-discharge consultations, especially during the initial recovery phase.
Why Choose India for Autologous Stem Cell Transplant?
India has become a global destination for autologous stem cell transplant due to its unique combination of medical excellence, advanced infrastructure, affordable pricing, and patient-centric services. International patients from Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and even parts of Europe are increasingly choosing India for life-saving stem cell therapies.
Here are the top reasons why India stands out:
- Globally Renowned Hematologists and Transplant Specialists: India is home to internationally trained and highly experienced specialists, such as Dr. Rahul Bhargava, who are pioneers in bone marrow transplant procedures. These experts are highly skilled in treating complex blood cancers and are actively involved in research and innovation in transplant medicine.
- Advanced Medical Infrastructure: Top hospitals in India, such as the Fortis Memorial Research Institute (FMRI) in Gurgaon, are equipped with cutting-edge technology, HEPA-filtered transplant units, high-end diagnostic laboratories, and critical care facilities. These institutions adhere to strict international safety standards, thereby minimizing the risk of infection and enhancing outcomes.
- High Success Rates: Autologous transplants in India achieve success rates comparable to those in Germany or Europe, with multiple myeloma and lymphoma cases demonstrating 80-90% post-transplant survival when performed at the optimal time and under expert guidance.
- Significantly Lower Cost: India offers high-quality treatment at just 20% to 30% of the cost charged in developed nations. The affordability does not come at the expense of quality, making it an ideal destination for patients who seek value without compromise.
- Minimal Waiting Time: Unlike Western countries, where scheduling a transplant can take months, Indian hospitals offer fast-track admission, stem cell mobilization, and treatment initiation, which is crucial for patients needing urgent care.
- Comprehensive Post-Transplant Care: India's top centers offer long-term follow-up, nutritional counseling, and even telemedicine support after discharge. It ensures ongoing care and guidance, even after the patient returns home.
- Favorable Medical Visa and Travel Policies: India's medical visa process is efficient and well-integrated with hospital systems. Patients can expect quick approvals, visa extensions if needed, and personalized support with airport transfers and stay arrangements.
Common Myths and Facts About Autologous Stem Cell Transplant
Many misconceptions surrounding stem cell transplants can cause unnecessary fear or hesitation. Some common myths and the facts related to autologous stem cell transplant are:
Myth: The procedure is extremely painful.
Fact: The transplant itself feels like a simple IV infusion. While chemotherapy may cause side effects, patients are well-supported with medication and care to manage any discomfort.
Myth: Stem cells are taken from the spine or bone marrow only.
Fact: In most cases, peripheral blood stem cells are collected from a vein using a process called apheresis, which is safe and painless.
Myth: There is a high chance the body will reject the cells.
Fact: Since the cells are from the patient's own body, there is no risk of rejection or graft-versus-host disease.
Myth: India may not have safe facilities for transplants.
Fact: India is home to accredited transplant centers equipped with HEPA-filtered units, robust infection control protocols, and outcomes that meet global standards.
What Services are Available for International Patients in India?
India offers a comprehensive and well-organized support system for international patients undergoing autologous stem cell transplants. From the initial consultation to post-discharge follow-ups, every aspect of the medical journey is designed to be smooth, affordable, and patient-friendly.
- Dedicated International Patient Helpdesks: Hospitals in India have specialized departments that cater exclusively to foreign patients. These teams assist with everything—from travel planning and appointment scheduling to daily coordination during the hospital stay.
- Medical Visa Assistance: Hospitals provide patients with a visa invitation letter and a treatment plan, which helps expedite the Indian medical visa process. If needed, they also help extend the visa for longer treatment durations.
- Airport Pick-Up and Local Transportation: To ensure comfort and safety, hospitals or partnered service providers arrange airport pick-up and drop-off, as well as local transport to and from the hospital or accommodation.
- Language Interpretation Services: For patients from non-English-speaking countries, interpretation services are available in Arabic, French, Amharic, Swahili, and other languages. It ensures clear communication with doctors and nurses at every stage of care.
- Accommodation and Food Assistance: Hospitals assist international families in finding safe, hygienic, and affordable accommodations near the medical center. On-campus guest houses or service apartments may also be available. Meal services are customized to suit various cultural and dietary preferences, including halal, vegetarian, and African cuisine options.
- Financial Guidance and Transparent Billing: International patients are given detailed cost estimates in advance. Billing is transparent, with explicit inclusion of all services, including pre-transplant testing, medication, nursing, and hospital stay. Most hospitals accept wire transfers and credit cards as forms of payment.
- Family Support During Hospital Stay: A dedicated coordinator ensures that the patient's family or attendant is well-informed and supported throughout the treatment process. Guidance is provided on visiting hours, health updates, and local assistance.
- Post-Transplant Care and Teleconsultation: After discharge, hospitals offer remote follow-ups through video consultations, medication monitoring, and access to transplant specialists from their home country.
Patient Testimonials
Samuel D., Cameroon – Autologous Transplant for Multiple Myeloma
"My father was diagnosed with multiple myeloma and needed an autologous transplant. We could not afford treatment in Europe, so we turned to India. From the moment we arrived, the hospital team took care of everything. The doctors were skilled, the transplant unit was very clean, and we were updated daily. My father is now recovering well. Choosing India saved his life."
Mekdes T., Zambia – Hodgkin's Lymphoma Survivor
"After relapse from Hodgkin's lymphoma, I was told a transplant was my only hope. We contacted hospitals in India, and we received an immediate response. Within two weeks, I was in New Delhi undergoing treatment. The doctors explained every step, and the care was of the highest standard. I'm now back home, healthy, and hopeful. India was the best decision we made."
Zahra M., Iran – Affordable Care for Relapsed Lymphoma
"Autologous transplant costs were very high in my country. A family friend suggested India, and we found an excellent hospital with a strong hematology team. The process was smooth, and I was able to recover with proper follow-up care. The nurses and translators were very helpful. I recommend India to anyone looking for advanced cancer treatment."
Ali K., Yemen – Stem Cell Transplant After Chemotherapy Failure
"I had aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma that came back after chemotherapy. We were losing hope until we read about stem cell transplants in India. The team there gave me a second chance. Everything was done professionally, from stem cell collection to post-treatment care. Now I'm home and doing well. Thank you to the Indian doctors who gave me my life back.
Frequently Asked Questions
The success rate of autologous stem cell transplants in India ranges from 80% to 90%, particularly for co
The cost of an autologous stem cell transplant in India typically ranges between $20,000 and $30,000, depending on the hospital, disease type, duration of hospitalization, and post-treatment requirements.
Yes, many top Indian hospitals accept international insurance policies, especially those linked with global providers. However, insurance approval must be confirmed in advance. Patients are encouraged to contact the hospital's international desk to verify insurance compatibility, review documentation requirements, and explore cashless or reimbursement options.
International patients are advised to plan for a stay of around 6 to 8 weeks. It includes pre-transplant testing, stem cell collection, chemotherapy, the transplant itself, recovery, and early post-transplant follow-up care.
The actual stem cell transplant process is not painful, as it resembles a blood transfusion. However, some patients may experience side effects from high-dose chemotherapy, including fatigue, nausea, mouth sores, and temporary hair loss, which are managed with supportive care.
Yes. Hospitals in India provide assistance with finding clean, affordable accommodation, and many offer meal plans tailored to the cultural and dietary needs of international families, including halal and vegetarian options.
Absolutely. Most hospitals allow one attendant to stay with the patient or nearby. Family members are also supported with guidance on local transportation, accommodations, and navigating the hospital.
Yes. After collection, your stem cells are cryopreserved in state-of-the-art stem cell banks under strict temperature control and monitoring until they are reinfused during the transplant.
Autologous stem cell transplants carry fewer risks than donor (allogeneic) transplants. However, potential complications include infections, bleeding, delayed recovery, or organ stress from chemotherapy. The medical team closely monitors and manages these.
Yes. Most hospitals offer telemedicine services, allowing you to consult with your transplant specialist remotely for test reviews, medication adjustments, and ongoing monitoring after your return.