CAR-T Cell Therapy in India
Cancer is a severe disease that affects millions of people around the world. Some types of cancer, like blood cancers, can be hard to treat with regular methods such as chemotherapy or radiation. But there is a new, powerful way to fight cancer — CAR T-cell therapy.
CAR T-cell therapy is a special kind of immunotherapy. It uses the patient's own immune cells to find and kill cancer cells. This treatment has shown excellent results in patients with certain blood cancers.
India is now offering CAR T-cell therapy at a much lower cost than many Western countries. The cost of CAR T-cell therapy in India lies between USD 45,000 to USD 60,000. Indian hospitals offer skilled doctors, advanced laboratories, and robust support services for international patients. That's why an increasing number of people from abroad are choosing India for this treatment.
What Is CAR T-Cell Therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy stands for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy. It is a type of immunotherapy. That means it helps your body's own immune system fight cancer.
In this treatment, doctors take T-cells (a type of white blood cell) from your blood. These T-cells are changed in a lab. The change allows them to find better and kill cancer cells. The new, powerful cells are then put back into your body to attack the cancer.
This method differs significantly from chemotherapy or radiation. Instead of killing healthy cells, it targets only the cancer cells. That's why it's often used when other treatments don't work or when cancer comes back.
How Does CAR T-Cell Therapy Work? Step-by-Step Process
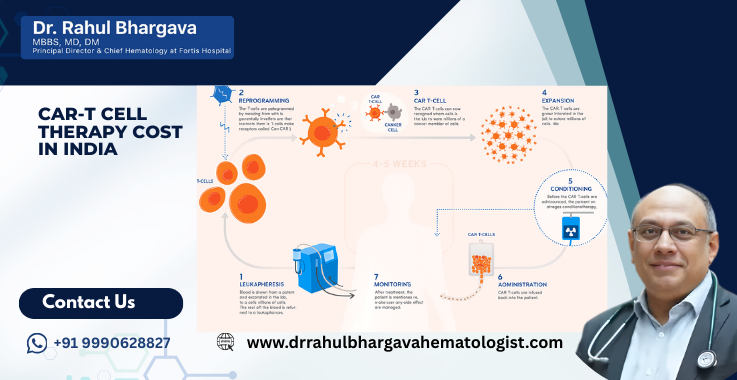
The complete CAR T-cell therapy process takes several weeks. It happens in stages. Here is a simple step-by-step guide to how it works:
- T-Cell Collection (Leukapheresis): Doctors take blood from your body using a machine. The machine separates the T-cells. This process is safe and takes a few hours.
- T-Cell Engineering: The T-cells are sent to a lab. In the lab, a special gene is added to the T-cells. This gene creates the CAR (Chimeric Antigen Receptor). The CAR helps the T-cells recognize cancer cells.
- Cell Multiplication: The new CAR T-cells are grown in large numbers in the lab. It can take 2–3 weeks.
- Conditioning Chemotherapy: Before giving the new cells, doctors give mild chemotherapy. It creates space in the body for the CAR T-cells to function more effectively.
- CAR T-Cell Infusion: The lab-made CAR T-cells are put back into your bloodstream. It is done in a hospital under careful monitoring.
- Recovery and Monitoring: Doctors watch for side effects and signs of improvement. You may stay in the hospital for a few days or weeks.
Which Cancers Are Treated with CAR T-Cell Therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is most effective for certain types of blood cancer. It is mainly used when the cancer has come back (relapsed) or has not responded to other treatments.
Cancers Treated with CAR T-Cell Therapy:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Especially in children and young adults.
- Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): A fast-growing form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Primary Mediastinal B-cell Lymphoma
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
- Multiple Myeloma: Some cases with FDA-approved CAR T therapies
Doctors in India may recommend CAR T-cell therapy only after checking your medical history, reports, and type of cancer. It is not suitable for all patients.
NexCAR19 (ImmunoACT)? – India's First Indigenous CAR T-Cell Therapy
India took a significant step forward in cancer care with the launch of NexCAR19, the country's first homegrown CAR T-cell therapy. It was developed by ImmunoACT, a company incubated at IIT Bombay, in partnership with Tata Memorial Centre and Apollo Hospitals.
NexCAR19 is designed to treat B-cell cancers, especially B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These are the same types of blood cancers treated with CAR T-cell therapy in the USA.
Why Is NexCAR19 Important?
- It offers affordable access to a life-saving therapy that previously relied on imported, expensive options.
- It is made using Indian biotechnology and clinical expertise.
- It received market authorization from India's drug regulator (CDSCO) in 2023 after successful trials.
- It is now available in select hospitals in India under strict safety protocols.
Why Choose India for CAR T-Cell Therapy?
Many international patients are choosing India for CAR T-cell therapy for several reasons:
- Affordable Costs: India offers the same quality treatment at much lower prices.
- World-Class Doctors: Indian oncologists such as Dr. Rahul Bhargava are highly trained and globally recognized.
- Modern Technology: Hospitals use the latest diagnostic and treatment tools.
- Shorter Waiting Times: Patients receive treatment more quickly than in the United States or the United Kingdom.
- International Patient Support: Hospitals offer assistance with visas, accommodations, travel arrangements, and translation services.
- Personalized Care: You get one-on-one care and support at every step.
Cost of CAR T-Cell Therapy in India
CAR T-cell therapy is one of the most advanced cancer treatments available today. Because it involves lab-engineered immune cells, the process is complex and expensive. However, in India, this treatment is far more affordable than in the United States or Europe. The average CAR T-cell Therapy Cost in India is USD 45,000 to USD 60,000 (INR 30 to INR 50 lakhs), depending on the type of cancer, hospital, and treatment plan.
This is significantly less than the cost in Western countries, where it can exceed USD 500,000 or more. India has recently developed indigenous CAR T-cell products, which have further reduced the price.
Cost Comparison: India vs Other Countries
Understanding the global cost difference helps international patients make wise choices. Many countries offer this therapy, but their prices are very high. India provides similar quality care at a fraction of the cost. Here's how India compares to other leading medical destinations.
| Country | Average Cost(USD) |
| India | USD 45,000 – USD 60,000 |
| USA | USD 400,000 – USD 500,000+ |
| UK | USD 350,000 – USD 450,000 |
| Germany | USD 300,000 – USD 450,000 |
| Turkey | USD 100,000 – USD 200,000 |
| South Korea | USD 150,000 – USD 250,000 |
India offers 70–90% savings compared to top global hospitals — with no compromise on quality.
What Is Included in the Cost of CAR T-cell Therapy in India?
Before choosing a hospital, it's essential to know what's included in the treatment package. Most hospitals in India offer precise and complete cost estimates. It helps international patients budget their trips and avoid surprise charges. Here's a list of what's usually included and what's not.
Usually Included:
- Medical evaluation and consultations
- Blood tests and genetic profiling
- T-cell collection and lab engineering
- Conditioning chemotherapy
- CAR T-cell infusion
- Hospital stay (usually 10–21 days)
- Monitoring and nursing care
- Basic supportive medications
Not Typically Included:
- Complication management (e.g., ICU care if needed)
- Repeat hospitalization
- Flight tickets, travel insurance
- Extra hotel stays for family or caregivers
- Post-treatment PET scans after discharge
Before starting, the hospital will provide a detailed cost estimate with a breakdown of what is included. Always ask for this information before planning your trip.
Factors That Affect the Cost of CAR T-cell Therapy in India
The cost of CAR T-cell Therapy can vary depending on several personal and medical factors. Knowing these in advance helps patients plan better. From the type of cancer to hospital stay, each factor adds to the final cost. Let's explore the most common reasons for cost changes.
- Type of Cancer: Some cancers need more complex or custom CAR T-cell designs.
- Hospital Chosen: Premium hospitals in metro cities may cost slightly more.
- Type of CAR T-Cell Product: Indigenous (local) products are cheaper than imported ones.
- Patient's Condition: If complications arise, ICU or extended care may increase the cost.
- Additional Tests: Advanced scans or gene sequencing may incur an extra cost.
- Duration of Hospital Stay: Longer stays due to side effects will increase expenses.
- Post-Treatment Monitoring: Some patients may require 2–3 follow-up visits or additional medications.
Timeline of the CAR T-Cell Therapy Process
CAR T-cell therapy doesn't happen in one day. It takes several weeks to complete, as the cells need to be collected, engineered, and then infused. Here's a simple breakdown of the entire process, from start to recovery.
| Stage | Time Duration |
| Medical Evaluation & Tests | 3–5 days |
| T-cell Collection (Leukapheresis) | 1 day |
| Cell Engineering in Lab | 2–3 weeks |
| Conditioning Chemotherapy | 3–4 days |
| CAR T-Cell Infusion | 1 day |
| Hospital Monitoring | 7–14 days (or more) |
| Discharge & Rest | 7–10 days (nearby stay) |
The total duration from start to finish is 6 to 8 weeks (depending on the patient's condition and hospital protocol).
Recovery After CAR T-cell Therapy
Recovery is a crucial component of the CAR T-cell therapy journey. After the cells are infused into your body, doctors will monitor you closely. It helps ensure the treatment works well and catches any early side effects. Most patients require hospitalization for a few weeks after the infusion.
Here is what to expect during the recovery phase:
- Hospital Stay After Infusion: You may stay in the hospital for 7 to 14 days after CAR T-cell infusion. During this time, doctors will check your temperature, heart rate, and oxygen levels. Nurses monitor your symptoms around the clock.
- Side Effect Monitoring: Some patients may experience side effects, such as fever, fatigue, or low blood pressure. A rare but serious side effect is cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Doctors are trained to handle these issues quickly and safely.
- Infection Prevention: Your immune system is weak after therapy. You'll be in a clean room to avoid infections. Doctors may give antibiotics or other medicines to protect you.
- Rest and Nutrition: You may feel tired and need extra rest during this period. The hospital offers healthy, soft meals to support recovery and healing. Drinking water and staying active (as advised) help recovery.
- Follow-up Tests: Blood tests will be performed regularly to monitor your body's response to the treatment. A PET or CT scan may be done before you return home. If all is well, doctors will prepare your discharge plan.
- Stay in India After Discharge: Even after hospital discharge, you should stay nearby for 7–10 more days. This allows the doctors to manage any delayed side effects. International patients usually plan a 4–6 week stay in total.
- Follow-Up After Returning Home: You will receive a detailed treatment summary and follow-up plan. Indian hospitals also offer teleconsultation for future updates. Share your medical report with your home doctor for continued care.
Benefits and Risks of CAR T-Cell Therapy
CAR T-cell therapy is a powerful and promising treatment for certain types of blood cancer. It works in a completely different way compared to chemotherapy or radiation. But, like any advanced therapy, it comes with both benefits and risks. Let's understand both clearly.
Benefits of CAR T-Cell Therapy
CAR T-cell therapy has shown success, whereas other treatments have failed. It is beneficial for patients whose cancer has returned after treatment or did not respond to standard care. Here are the main benefits:
- High Success Rate: Many patients achieve remission (no signs of cancer) after one treatment.
- Targeted Action: It attacks only cancer cells, not healthy ones. This reduces long-term damage to the body.
- Fewer Long-Term Side Effects: Unlike traditional chemo, CAR T-cell therapy often has fewer lasting side effects.
- One-Time Treatment: In most cases, it involves a single infusion rather than months of therapy.
- Hope for Relapsed Patients: It offers a chance of survival to patients who have no other options.
- FDA-Approved Worldwide: It is approved in the USA, UK, and Europe and is now available in India.
Risks and Side Effects of CAR T-Cell Therapy
While the therapy can be life-saving, it also comes with some risks. These side effects are usually manageable in experienced hospitals, such as those in India. Here are the main risks:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): This is a common side effect. It can cause fever, low blood pressure, or trouble breathing. Doctors treat it with special drugs.
- Neurological Symptoms: Some patients may experience confusion, drowsiness, or speech difficulties. These are usually temporary and monitored closely.
- Low Blood Counts: After therapy, your blood cell levels may drop. You may need transfusions or injections to help you recover.
- Infections: Because your immune system is weak for a while, you may be at risk of infection. Doctors will give antibiotics if needed.
- Organ Stress (Rare): Some patients may experience stress on organs such as the liver or kidneys. This is rare and usually reversible.
Why Choose India for CAR T-Cell Therapy?
India is becoming a trusted destination for advanced cancer care, including CAR T-cell therapy. The country offers the same treatment available in the USA or UK—at a much lower cost. Indian hospitals, such as Fortis Memorial Research Institute in Gurgaon, are renowned for their experienced doctors, state-of-the-art facilities, and patient-centered care. Here are the top reasons international patients choose India:
- Affordable Treatment: CAR T-cell therapy in India costs up to 80% less than in Western countries. Indian hospitals now offer both imported and indigenous CAR T-cell options. You save money without compromising on quality.
- Expert Doctors: Indian oncologists are trained in top global institutions. Many have years of experience treating blood cancers and doing cellular therapy. Hospitals follow international safety protocols.
- Shorter Waiting Times: In India, treatment can begin within 2–3 weeks. There are no long waitlists like in the US, UK, or Canada.
- Multilingual Support: Interpreters are available in Arabic, Russian, French, Swahili, and more. Written reports and prescriptions can be translated for your local doctor.
- Telemedicine and Follow-Up: After returning home, patients can consult doctors online. Hospitals offer free or low-cost teleconsultation for follow-ups.
Support Services for International Patients
Traveling to another country for treatment can feel overwhelming. Patients visiting Dr. Rahul Bhargava receive dedicated assistance through Fortis Memorial Research Institute, ensuring a smooth and stress-free medical journey. Here’s what international patients can expect:
Visa Assistance:
The hospital provides a medical visa invitation letter, usually within 24–48 hours, and guides patients through the visa application process.
Airport Pickup and Drop:
Patients are assisted with airport pickup and drop services, ensuring comfortable and safe transfers between the airport, hospital, and accommodation.
Help with Accommodation:
The hospital team helps arrange nearby hotels, guesthouses, or serviced apartments based on patient preferences and budget, making long-term stays convenient for patients and attendants.
Interpreters and Translators:
Language interpreters are available to help patients communicate with doctors and staff. Medical reports and discharge summaries can also be provided in translated formats if required.
Food and Prayer Needs:
The hospital supports dietary preferences and offers options suitable for international patients, including special meal requests. Prayer facilities and culturally appropriate food options are also available.
Easy Payment Options:
International patients can make payments through wire transfer, international cards, or other accepted payment methods. Billing is transparent, with proper estimates shared in advance.
Tip:
Since treatment is coordinated through Fortis, the international patient support team assists with all arrangements so patients and families can focus entirely on recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Patients with certain blood cancers, such as leukemia or lymphoma, may qualify. Doctors will review your reports to determine if you're suitable for this treatment
You'll need approximately 4 to 6 weeks in total, including the hospital stay and post-infusion monitoring
Yes, it is generally safe when done in expert centers. Side effects are possible but well managed in Indian hospitals
Yes. Especially for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The doctor will determine the treatment based on the patient's age, weight, and medical condition.