Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Treatment in India
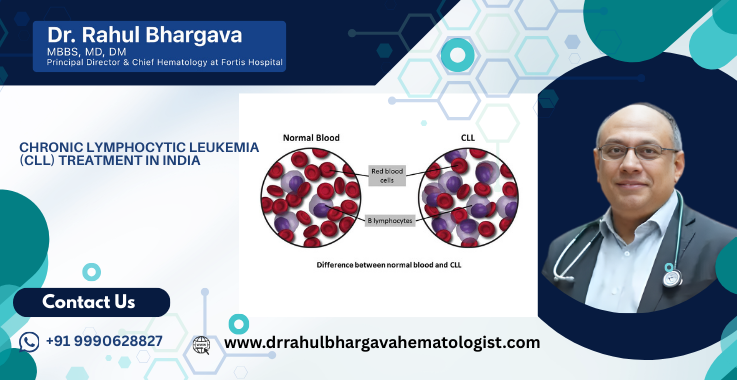
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, or CLL, is a common type of adult leukemia that starts in your bone marrow and develops slowly. Because it often progresses quietly, many people do not notice symptoms until later stages. CLL can significantly affect your immune system and overall health over time.
India has quietly become a popular destination for treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Many hospitals offer high-quality care at a fraction of the cost compared to Western countries. The cost of chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment in India ranges from USD 4,000 to USD 35,000. Patients from the UAE, UK, US, Africa, and Southeast Asia travel to India each year for CLL treatment, including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and even stem cell transplant.
What Is Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow. It usually affects older adults and develops more slowly than other forms of leukemia. In CLL, the marrow produces too many abnormal white blood cells, specifically a type called lymphocytes. These abnormal cells accumulate over time and do not function properly.
How CLL Affects the Body
In a healthy person, white blood cells help fight infections. However, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the cancerous lymphocytes do not fight infection effectively. As their numbers grow, they crowd out the healthy blood cells your body requires to function normally. It can cause:
- Anemia: Due to a drop in healthy red blood cells, leading to tiredness and weakness.
- Infections: Because abnormal lymphocytes cannot fight bacteria and viruses well.
- Bleeding or bruising: When the platelet count is low, blood clotting becomes a problem.
- Swollen lymph nodes: You may notice lumps in the neck, armpits, or groin.
- Enlarged spleen or liver: You might feel fullness or discomfort in the belly.
- Weight loss and night sweats: These may appear as the disease progresses.
Types of CLL
There are two major types of chronic lymphocytic leukemia based on how fast the cancer cells grow and behave:
- Slow-growing (indolent) CLL – Most patients have this form. It may not require treatment immediately, but regular monitoring is crucial.
- Fast-growing (aggressive) CLL – This form progresses quickly and usually requires immediate treatment.
Who Is at Risk for CLL?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is most common in people over the age of 60. It is rarely seen in children or young adults. Men are more likely to develop CLL than women. Risk factors include:
- A family history of leukemia or lymphoma
- Exposure to certain chemicals (like Agent Orange)
- Being of European descent (it is less common in Asian or African populations)
However, many people diagnosed with CLL do not have any clear risk factors.
Common Symptoms of CLL
In its early stages, chronic lymphocytic leukemia might not cause any noticeable symptoms. Some people discover they have it during a routine blood test. As the disease progresses, you may experience:
- Persistent fatigue or weakness
- Frequent infections
- Swollen glands in the neck or groin
- Pain or fullness in the upper abdomen (due to an enlarged spleen)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats or fever
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Shortness of breath
If you notice any of these symptoms for more than a few weeks, it's essential to get medical attention.
Diagnosis and Staging of CLL in India
Getting an accurate diagnosis is the first step toward proper treatment. In India, major hospitals, such as Fortis Memorial Research Institute in Gurgaon, offer advanced and reliable testing for CLL. Indian doctors follow international guidelines to diagnose and stage the disease before creating a personalized treatment plan.
How CLL Is Diagnosed?
Oncologists use a combination of blood tests and imaging to confirm CLL. You may undergo the following:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test checks the number and types of cells in your blood. CLL is often suspected when there's a high number of white blood cells—especially lymphocytes.
- Peripheral Blood Smear: A pathologist examines a drop of blood under a microscope to look for abnormal lymphocytes. This test gives a clearer picture of how the cells look.
- Flow Cytometry: This advanced test checks the surface markers of white blood cells to confirm the presence of CLL. It is a key diagnostic tool used widely in Indian hospitals.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy (if needed): A small sample of bone marrow may be taken from the hip bone to see how deeply CLL has affected the marrow.
- Genetic and Molecular Testing: Tests such as FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization) and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) help detect specific gene mutations, like del(17p) or TP53, which affect prognosis and treatment response.
- Imaging Tests: Doctors may use CT scans and ultrasounds to check for enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, or liver.
CLL Staging
Once CLL is confirmed, doctors use staging systems to determine the stage of the disease. India follows the same global standards, primarily the Rai System (used in the US) and the Binet System (used in Europe).
Rai Staging System (used in India for international patients):
- Stage 0: High lymphocyte count but no other symptoms. It often needs monitoring only.
- Stage I-II: Lymph nodes are enlarged. You may also have anemia or an enlarged spleen or liver.
- Stage III-IV: Anemia or low platelet count is present. Treatment is typically required.
Why Diagnosis in India Is Reliable
Top cancer centers in India are equipped with modern labs, hematopathologists, and machines that meet international standards. Many doctors are US or UK board-certified and follow NCCN or ESMO treatment protocols. It ensures that you receive a diagnosis that is both fast and globally accepted.
Diagnosis in India is also cost-effective. While in the US, these tests can cost over USD 3,000–USD 5,000; in contrast, Indian hospitals offer a comprehensive diagnostic package starting from USD 300 to USD 800, depending on the hospital and location.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Treatment and Cost in India
India is one of the most preferred countries for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment due to its advanced medical facilities, experienced specialists, and affordable pricing. Hospitals like Fortis Memorial Research Institute in Gurgaon, led by doctors such as Dr. Rahul Bhargava, offer world-class cancer care while saving patients 60–80% compared to Western countries.
Observation or Watchful Waiting
For many patients with early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia, immediate treatment is not necessary. If you don't have any severe symptoms, your doctor may recommend a strategy called "watchful waiting." It means your condition will be monitored regularly through blood tests and physical checkups.
You may only need treatment if symptoms begin to appear or if the disease starts to progress. This approach avoids unnecessary medication and side effects.
In India, the cost of this regular monitoring is quite affordable. Each doctor consultation costs around USD 30 to USD 50 and routine blood tests can be done for about USD 20 to USD 40. On average, the yearly cost of watchful waiting in India ranges from USD 200 to USD 500.
Chemotherapy for CLL
Chemotherapy is often the first line of treatment for CLL, especially in younger and fit patients. It involves the use of potent drugs that kill or stop the growth of cancerous cells. Common chemotherapy drugs used for CLL include Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide, and Bendamustine.
Chemotherapy is given in cycles, with each cycle lasting about 3 to 4 weeks. Most patients receive around 4 to 6 cycles in total.
In India, each chemotherapy cycle costs between USD 600 and USD 1,500, depending on the type of drugs used, the hospital, and whether the treatment is administered in a general ward or a private room. Therefore, the total cost for a complete chemotherapy course in India ranges from USD 2,500 to USD 6,000. Indian hospitals often deliver chemotherapy in outpatient day-care centers, which keeps costs lower and makes treatment more comfortable for patients.
Targeted Therapy for CLL
Targeted therapy is a newer and more effective way to treat CLL, especially in patients with specific genetic mutations like TP53 deletion or those who cannot tolerate chemotherapy. These medicines target particular proteins that cancer cells rely on for growth and survival.
In India, the most commonly used targeted therapies for CLL include:
- Ibrutinib (a BTK inhibitor)
- Venetoclax (a BCL-2 inhibitor)
- Idelalisib (used less frequently)
These medications are typically taken as oral tablets, either once daily or in divided doses throughout the day. Treatment may last for several months or even years, depending on the patient's response.
Imported versions of these medicines can be expensive, costing around USD 1,000 to USD 2,000 per month. However, India also produces high-quality generic versions that are significantly more affordable. This can reduce the monthly cost by 40% to 60%.
On average, the yearly cost of targeted therapy in India ranges from USD 10,000 to USD 20,000, depending on the drug used and the length of treatment.
Immunotherapy for CLL
Immunotherapy boosts the body's natural immune system to fight cancer. In CLL, doctors often use monoclonal antibodies, such as Rituximab or Obinutuzumab. These medicines target and destroy specific cells that carry the cancer.
Immunotherapy is often combined with chemotherapy or targeted therapy for better results. The drugs are given through an IV (intravenous) drip, usually once a week or every few weeks.
Each dose of immunotherapy in India costs between USD 1,000 and USD 2,500. Most patients receive 4 to 6 doses as part of their treatment plan. So, the total cost of immunotherapy can range from USD 4,000 to USD 10,000.
Many Indian hospitals offer biosimilar versions of these drugs. These are just as effective as the original brands but cost much less, helping to reduce the overall cost of treatment.
Stem Cell Transplant for CLL
Although it is not needed for every patient, a stem cell transplant (also called a bone marrow transplant) may be recommended in certain high-risk or relapsed CLL cases. It is mainly considered for younger patients who have aggressive disease or do not respond well to other treatments.
India is a preferred destination for stem cell transplants, offering top-quality facilities and international-level care at significantly lower prices than those in the US or Europe. The procedure involves replacing damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a donor.
In India, an allogeneic stem cell transplant (where stem cells come from a donor) typically costs between USD 15,000 and USD 30,000. It includes the pre-transplant evaluation, donor search and matching, high-dose chemotherapy, hospital stay (often 3 to 4 weeks), ICU care, medications, and post-transplant follow-ups.
Supportive Care During and After Treatment
CLL patients may need additional care to manage side effects or infections during treatment. It is known as supportive care and plays a vital role in recovery and improving quality of life.
Some of the common supportive treatments include:
- Blood transfusions to treat anemia – Each unit costs about USD 50 to USD 100
- Growth factor injections like G-CSF to boost white cell count – USD 100 to USD 300 per shot
- Antibiotics or antifungal medicines to prevent infections – USD 20 to USD 100 per course
- Nutritional therapy or IV fluids if the patient is weak – USD 30 to USD 100 per day
- Regular doctor visits and monitoring – USD 30 to USD 50 per visit
Depending on the patient's condition, supportive care over 6 to 12 months can cost between USD 500 and USD 2,00.
Total Estimated Cost of CLL Treatment in India
|
Treatment Type |
Estimated Cost (USD) |
|
Observation / Monitoring |
USD 200 – USD 500/year |
|
Chemotherapy (full course) |
USD 2,500 – USD 6,000 |
|
Targeted Therapy (annually) |
USD 10,000 – USD 20,000 |
|
Immunotherapy with chemo |
USD 5,000 – USD 12,000 |
|
Bone Marrow Transplant (if required) |
USD 18,000 – USD 30,000 |
|
Additional supportive care |
USD 500 – USD 2,000 |
|
Complete Package (with travel/stay) |
USD 4,000 – USD 35,000 |
Factors That Affect the Cost of CLL Treatment in India
The total cost of treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia can vary from patient to patient. This is because several essential factors influence the final expense.
- Type and Stage of CLL: The cost depends heavily on whether your CLL is in an early or advanced stage. In the early stages, patients might not need immediate treatment, just regular monitoring (called "watchful waiting"). It is very cost-effective. But for more advanced cases, active treatment begins—often with targeted therapies or chemotherapy—which increases the overall cost.
- Choice of Treatment: Different treatment options come with different price tags. Targeted therapy drugs like ibrutinib and venetoclax are highly effective but more expensive. Chemotherapy (such as the FCR regimen) is more affordable but may require more hospital visits and supportive care. Immunotherapy like Rituximab is often used with chemo, which raises the cost slightly. Stem cell transplant, though not common in CLL, is the most expensive option and includes pre-transplant tests, hospital stays, and long-term follow-up.
- Duration of Treatment: Certain treatments, such as chemotherapy, are administered over a period of 3 to 6 months. Others, like targeted oral drugs, may need to be taken for many months or even years. The longer the treatment, the higher the cumulative cost.
- Room Category and Length of Stay: The cost of hospitalization varies depending on whether you choose a general ward, semi-private, or deluxe room. A more extended hospital stay—especially during chemotherapy or transplant—will naturally increase accommodation and nursing charges.
- Supportive Medications and Tests: In addition to the primary treatment, patients may require blood tests and scans (CT, PET-CT), antibiotics or antivirals to prevent infections, blood transfusions (if blood counts drop), and growth factors or anti-nausea medications. These add to the overall treatment expense but are essential for comfort and safety.
- Availability of Generic vs. Branded Drugs: In India, patients often have the choice between internationally branded medicines and high-quality Indian generics. Branded drugs are more expensive, but many Indian generics are equally effective and widely used, significantly reducing the overall cost.
Recovery, Success Rates, and Post-Treatment Care for CLL in India
India has become a trusted destination for CLL treatment due to high medical standards, modern infrastructure, and expert oncologists. Patients not only receive world-class care, but they also benefit from more affordable treatment options and personalized follow-up plans. Understanding what recovery entails, how successful the treatments are, and what care is required afterward can help you or your loved one feel more prepared and confident.
Recovery After CLL Treatment
Recovery from CLL treatment varies based on the type of therapy received, the stage of the disease, and the patient's overall health. Because CLL is typically a chronic condition, the main aim of treatment is to effectively manage the disease and extend quality of life rather than to "cure" it completely in most cases.
- After chemotherapy, most patients may take several weeks to regain their energy. Adverse effects such as fatigue, nausea, and lowered immunity may gradually improve over 2 to 4 weeks after each cycle.
- For targeted therapy, many patients report faster recovery and fewer side effects, especially when using oral medications like Ibrutinib or Venetoclax. Most people resume their regular activities within a few days of starting treatment.
- Immunotherapy may cause flu-like symptoms or allergic reactions during the infusion. These side effects usually fade within 24 to 48 hours, and recovery tends to be swift.
- After a stem cell transplant, recovery is more prolonged and more intensive. Patients may need to stay in India for 1 to 2 months for close monitoring and follow-up. Full recovery can take anywhere from 3 to 6 months or longer.
Patients are encouraged to rest, eat well, stay hydrated, and avoid crowded places to reduce the risk of infection. They should also keep all follow-up appointments. With support from India's skilled oncology teams, many patients can resume work and daily activities during or shortly after treatment.
Success Rates of CLL Treatment in India
Success in CLL treatment is not always measured by a complete cure but by disease control, longer remission, and good quality of life. The success rates in India are comparable to those in the United States and Europe, particularly at top-tier hospitals such as Fortis Memorial Research Institute in Gurgaon. Here are some general success rate insights:
- Chemotherapy and immunotherapy (such as the FCR regimen) have a remission rate of up to 70–80% in fit patients under 65 years. Complete remission (where no disease is detectable) is possible for many.
- Targeted therapy with Ibrutinib or Venetoclax shows excellent results. Long-term disease control is possible in over 85% of patients who respond to treatment. These drugs are beneficial for older adults or those with high-risk mutations.
- Stem cell transplantation, though used in fewer cases, offers a chance for long-term remission in younger patients. The survival rate after a successful transplant can be 60–70% or higher, depending on risk factors.
- For most patients with early-stage or slow-progressing CLL, overall life expectancy with proper treatment and monitoring is close to normal.
India's success in CLL care is due to high-quality diagnostics, access to international treatment protocols, experienced hematologists, and affordable access to life-saving drugs.
Post-Treatment Care and Monitoring
Even after the main treatment ends, CLL requires regular checkups to ensure the disorder is under control. This is because the disease can return or progress slowly over time. Post-treatment care in India includes:
- Regular blood tests, including complete blood count (CBC) and lymphocyte levels
- Physical exams to check for swollen lymph nodes or spleen enlargement
- Bone marrow biopsies or imaging scans, only when needed
- Monitoring for late side effects of chemotherapy or immunotherapy
- Psychological support and counseling, especially for long-term survivors
Doctors in India typically schedule follow-ups every 3 to 6 months, depending on the patient's progress. Most international patients receive a detailed care plan to share with their local doctors after returning home. Teleconsultations are also available for continued support.
India's hospitals also offer nutrition counseling, rehabilitation services, and support groups to help patients recover emotionally and physically after treatment.
Patient Testimonials – Real Stories of Healing
Hearing from patients who have gone through chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment in India can offer powerful reassurance. Many international patients have successfully undergone treatment at Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon, under the expert care of Dr. Rahul Bhargava. Here are some of their stories, shared with permission to inspire others:
James R., United Kingdom – "World-class treatment at one-third the price"
"I was diagnosed with CLL at 61. I looked into treatment options in the UK, but the wait times were long, and the cost of targeted therapy was too high. A friend suggested India, and after thorough research, I chose Fortis in Gurgaon. Dr. Rahul Bhargava explained everything so clearly—from diagnosis to drug options. I started on Ibrutinib, and within a few weeks, my symptoms had already started to improve. What amazed me was the care—not just from the doctor, but the whole team. I stayed in India for three weeks and felt fully supported throughout my stay. It truly felt like a home away from home. And yes, the cost was a fraction of what I would've paid back home."
Fatima H., Kenya – "I trusted my instincts and came to India"
"My husband was losing weight and feeling extremely tired. We later learned it was CLL. Treatment in Nairobi was limited, and I didn't want to take chances. We reached out to Fortis Hospital in Gurgaon and received a treatment plan from Dr. Rahul Bhargava within two days. The hospital was very clean, organized, and professional. We felt reassured from day one. My husband underwent chemotherapy and later started targeted medication. Dr. Bhargava is kind, patient, and highly knowledgeable. Today, my husband's condition is stable, and we are doing regular video follow-ups. Coming to India saved his life."
Ahmed S., Iraq – "The right choice for our family."
"When my father was diagnosed with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, we were overwhelmed. We consulted doctors in Baghdad, but they lacked experience with advanced therapies. We searched online and found Fortis Memorial Research Institute. Dr. Rahul Bhargava's credentials gave us confidence. From the moment we arrived, we were treated like family. The team helped with accommodation, translation, and every detail. My father received immunotherapy, and he responded well. We are now back home, but we continue our check-ins through telemedicine. I am grateful for the professionalism and humanity we experienced in India."
Maria D., Romania – "Peace of mind and expert care"
"As a single mother, it was terrifying to be diagnosed with leukemia. I needed care I could trust, but I also had to think about affordability. I read about Dr. Rahul Bhargava's experience with leukemia and bone marrow transplant. When I reached Fortis Hospital, everything was arranged—the airport pickup, hotel stay, and quick admission. My targeted therapy went smoothly. I always felt heard, not just treated. The nurses, the counselors, and Dr. Bhargava made me feel like a person, not just a patient. I'm now two years into remission and living life fully."
Frequently Asked Questions
CLL is usually not considered curable, especially in older adults. However, with modern treatments like targeted therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, it can often be managed effectively for many years. Many patients live long, healthy lives with proper monitoring and timely treatment.
The treatment duration depends on the therapy chosen. Chemotherapy may last for 3 to 6 months, while targeted therapy is often taken for longer periods—sometimes even years. Stem cell transplant, if needed, involves a stay of several weeks to a few months in India. Doctors customize the timeline based on each patient's health condition and disease stage.
Yes, many Indian hospitals follow strict international protocols for hygiene, infection control, and treatment safety. Reputed hospitals, such as Fortis Memorial Research Institute in Gurgaon, are accredited by global healthcare quality bodies like the JCI and NABH. International patients are treated in dedicated departments with personalized care and support.
Most of the standard CLL drugs—like Ibrutinib, Venetoclax, Rituximab, and others—are available in India. Patients can choose between international brands and Indian generics, depending on preference and budget. Indian generics are strictly regulated and widely used by both local and global patients due to their lower cost and high quality.
No, international patients do not need a referral. You can directly contact the hospital or medical tourism agency, and they will connect you with a hematologist or oncologist. Once your medical reports are reviewed, a treatment plan and cost estimate are usually shared within 24–72 hours.
Patients are typically asked to share a copy of their passport, recent medical reports (including blood tests, biopsy results, and scans), and details of any previous treatments. For the visa process, most hospitals will provide an official visa invitation letter. A medical visa is typically issued quickly and can be extended if required.
Yes, English is the primary language used in most Indian hospitals, particularly those catering to international patients. Doctors, nurses, and coordinators are fluent in English, and interpreter services are available in other languages, such as Arabic, Russian, French, or Spanish, as needed.
For chemotherapy or targeted therapy, patients may stay for 2 to 4 weeks for evaluation, initial treatment, and monitoring. For stem cell transplant, a more extended stay of up to 8 to 12 weeks is needed. Follow-up visits can often be done virtually, making it convenient for patients to return home sooner.
Yes, most hospitals in India allow a family member or attendant to stay with the patient. Many offer accommodation inside or near the hospital, including guest houses and serviced apartments. These are clean, safe, and equipped with kitchens, Wi-Fi, and other facilities to make extended stays comfortable.