Platelet Storage Pool Defects Treatment in India
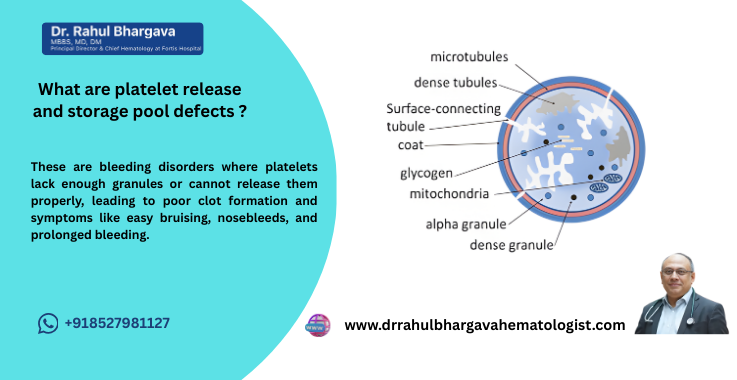
Platelet release and storage pool defects refer to a group of platelet disorders that result from abnormalities in the platelet's storage pools (specifically the alpha granules and dense granules) and the process of granule release during platelet activation. These defects impair the platelet's ability to effectively release substances necessary for blood clotting and wound healing, leading to a bleeding tendency or hemorrhagic symptoms.
Platelets are cell fragments in the blood that play a crucial role in stopping bleeding by forming blood clots. Inside platelets are specialized storage granules, including alpha granules, which store proteins like fibrinogen and platelet-derived growth factors, and dense granules, which store adenosine diphosphate (ADP), calcium, and serotonin—all of which are essential for platelet activation and aggregation.
When platelet function is impaired due to a defect in the release or storage of these granules, platelet aggregation and clot formation are compromised, resulting in bleeding disorders.
Platelet Release and Storage Pool Defects
Platelet release and storage pool defects are rare inherited or acquired bleeding disorders that affect the platelets’ ability to release essential substances during clot formation. Platelets play a critical role in blood clotting, and any disruption in their function can lead to excessive bleeding or bruising. Dr. Rahul Bhargava, an expert in hematology, explains that these defects are significant as they can cause recurrent and potentially dangerous bleeding episodes. Early diagnosis and proper management can greatly improve quality of life.
Causes of Platelet Release and Storage Pool Defects
There are two main types of platelet defects:
- Inherited causes: These are genetic disorders passed down from parents to children, often affecting proteins that control platelet release. Examples include Gray Platelet Syndrome and Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome.
- Acquired causes: Certain medications, autoimmune diseases, or medical conditions like leukemia can lead to acquired platelet release and storage pool defects.
Types of Platelet Defects
Dr. Rahul Bhargava identifies two primary categories of platelet defects:
- Dense Granule Storage Pool Deficiency: A lack of dense granules within platelets that store substances like ADP, ATP, and calcium, which are crucial for normal platelet function.
- Alpha Granule Storage Pool Deficiency: Involves a deficiency of alpha granules, which store proteins necessary for clot formation.
Symptoms of Platelet Release and Storage Pool Defects
Individuals with platelet defects often experience the following symptoms:
- Easy bruising
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Heavy menstrual periods (in women)
- Unexplained bleeding after surgery or dental procedures
- Petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin caused by bleeding)
If you notice these symptoms, Dr. Rahul Bhargava recommends seeking medical advice as soon as possible to prevent potential complications.
Diagnosis of Platelet Release and Storage Pool Defects
Diagnosing platelet disorders requires specialized blood tests and examinations. Dr. Bhargava’s approach includes:
- Complete blood count (CBC): To check platelet count and size.
- Platelet aggregation studies: To evaluate how well the platelets function.
- Electron microscopy: To visualize platelet granules and identify abnormalities.
- Genetic testing: For inherited cases, identifying genetic mutations can confirm the diagnosis.
Dr. Rahul Bhargava emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis for effective treatment planning.
Treatment for Platelet Release and Storage Pool Defects
While there is no cure for inherited platelet defects, treatment aims to manage symptoms and prevent bleeding complications. Dr. Bhargava’s treatment approach may include:
- Antifibrinolytic medications: To prevent the breakdown of blood clots.
- Platelet transfusions: In severe cases, platelet transfusions may be necessary to stop bleeding.
- Desmopressin (DDAVP): This medication can stimulate the release of stored substances from platelets in some patients.
- Hormonal therapy: For women with heavy menstrual bleeding.
Cost of Treatment and Stay in India
The cost of treating platelet release and storage pool defects in India is generally more affordable than in many Western countries, making it a favorable option for medical treatment. The total cost of treatment, including diagnosis, medication, and hospital stay, can vary based on the severity of the condition, the required tests, and the duration of care. Here’s an overview of the costs:
-
Initial Consultation:
USD: $30 – $100
INR: ₹2,200 – ₹7,400 -
Blood Tests and Diagnostic Procedures:
USD: $50 – $200
INR: ₹3,700 – ₹14,800 -
Platelet Transfusion (per session):
USD: $500 – $1,500
INR: ₹37,000 – ₹1,10,000 -
Antifibrinolytic Medications (per month):
USD: $50 – $200
INR: ₹3,700 – ₹14,800 -
Desmopressin (DDAVP) Treatment (per month):
USD: $100 – $500
INR: ₹7,400 – ₹37,000 -
Hospital Stay (per night):
USD: $25 – $150
INR: ₹2,000 – ₹11,100 per night
India offers high-quality healthcare services at competitive prices, making it a popular choice for individuals seeking treatment for bleeding disorders such as platelet release and storage pool defects. The costs are significantly lower compared to those in Western countries, yet the standard of care and advanced medical technology remain the same.
Frequently Asked Questions
Staying active, avoiding smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying hydrated are key preventive steps. If you’re at high risk, consult with a haematologist for personalized advice.
Yes, if left untreated, they can cause serious bleeding episodes. However, with appropriate treatment, these risks can be minimized.
Yes, Dr. Bhargava recommends genetic counseling for families, especially if there’s a history of bleeding disorders, to understand the risk of passing the condition to children.