Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Treatment in India
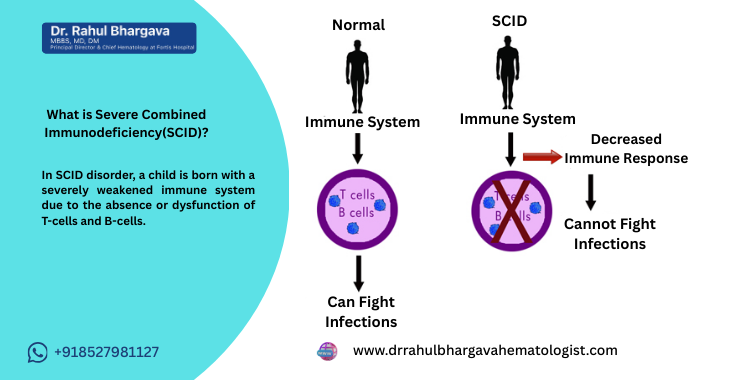
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) is a rare, life-threatening genetic disorder characterized by the absence or severe dysfunction of T-cells and B-cells, which are critical components of the immune system. This results in a severely weakened immune system, leaving affected individuals highly susceptible to infections. SCID is often referred to as the "bubble boy disease" because of the need for strict isolation and protection from infections.
SCID is diagnosed in infancy, usually in the first 6 months of life, when the infant starts to suffer from repeated, severe infections that are difficult to control. Without treatment, the condition is fatal, but with appropriate intervention, such as bone marrow transplant or gene therapy, affected individuals can have a normal or near-normal life expectancy.
What is Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)?
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) is a rare, life-threatening genetic disorder where a child is born with a severely weakened immune system. This condition leaves the body vulnerable to severe infections from bacteria, viruses, and fungi. SCID is often known as “bubble boy disease,” referencing the story of a child who had to live in a sterile environment due to the severity of his immune deficiency.
Types of Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
There are several types of SCID, classified based on the specific genetic mutation that causes the disorder. These include:
- X-linked SCID: The most common type, caused by mutations in the IL2RG gene on the X chromosome.
- Autosomal recessive SCID: This includes mutations in various genes such as ADA (adenosine deaminase deficiency), RAG1/RAG2 (recombination activating genes), and others.
- JAK3 deficiency: A rare form of SCID where the body cannot produce a specific enzyme needed for immune system function.
- CD3 deficiency: A rare form where T-cells, a key component of the immune system, are nonfunctional.
Each type can result in varying degrees of immune system dysfunction and requires specific treatment approaches.
Causes of Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
SCID is primarily caused by genetic mutations that affect the development and function of immune cells, particularly T-cells, B-cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. These mutations can be inherited from parents, and in some cases, they can occur spontaneously. The condition is typically diagnosed in early infancy due to the severe, recurrent infections it causes.
Symptoms of Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
The symptoms of SCID can vary based on the specific genetic mutation, but common signs include:
- Frequent and severe infections: These may include viral, bacterial, and fungal infections that are difficult to treat.
- Chronic diarrhea and failure to thrive: Infants with SCID may not gain weight as expected and experience digestive issues.
- Skin rashes: Some babies with SCID develop rashes that don’t resolve with treatment.
- Severe respiratory distress: Due to infections in the lungs or airways.
- Enlarged lymph nodes and spleen: In some cases, SCID can lead to lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly.
Without treatment, children with SCID may not survive past their second year due to complications from infections.
How is Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of SCID typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests, including:
- Newborn screening: In many countries, newborns are screened for SCID, which involves measuring T-cell receptor excision circles (TRECs) in the blood.
- Blood tests: These can confirm the deficiency of immune cells like T-cells, B-cells, or NK cells.
- Genetic testing: Identifying the specific genetic mutation responsible for SCID helps in determining the exact type of condition and tailoring treatment.
If SCID is suspected, early diagnosis is critical for timely intervention, as prompt treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
Treatment for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
Treatment for SCID focuses on restoring the immune system and preventing life-threatening infections. Common treatments include:
- Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT): The most effective treatment for SCID, BMT involves replacing the defective bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a compatible donor. This procedure can help restore the immune system and enable the body to fight infections.
- Gene Therapy: In cases like ADA-SCID, gene therapy has shown promise by inserting a healthy copy of the defective gene into the patient’s cells.
- Immunoglobulin Therapy: Infusions of immunoglobulins (antibodies) can provide passive immunity and help protect against infections while the immune system is being rebuilt.
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (for ADA-SCID): In ADA-SCID, enzyme replacement therapy may be used to manage the disease and improve immune function.
- Antibiotics and Antifungals: To prevent and treat infections, which are a common concern in SCID patients.
Why Choose Dr. Rahul Bhargava for SCID Treatment?
Dr. Rahul Bhargava is a renowned hematologist with extensive expertise in treating complex immunodeficiencies like Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID). Here’s why you should choose Dr. Bhargava:
- Expert Care: Dr. Bhargava is one of the leading specialists in immunology and hematology with years of experience in managing rare genetic disorders.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Each patient’s condition is unique, and Dr. Bhargava ensures a tailored approach to provide the best possible outcomes for SCID treatment.
- Advanced Techniques: With access to the latest medical technologies and cutting-edge treatments, including gene therapy and bone marrow transplantation, Dr. Bhargava offers state-of-the-art care.
- International Patient Care: Dr. Bhargava has treated patients from all over the world, ensuring that your treatment journey is smooth and stress-free.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Dr. Bhargava works closely with a team of specialists, including pediatricians, immunologists, and transplant surgeons, to provide comprehensive care.
Cost of SCID Treatment and Stay in India
India is a popular destination for medical treatment due to its world-class healthcare infrastructure and affordable treatment options. The cost of treating Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) in India varies depending on the type of treatment required. Below are the general estimates in both USD and INR:
- Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT):
- USD: $20,000 to $50,000
- INR: ₹15,00,000 to ₹37,50,000
- Gene Therapy:
- USD: $25,000 to $60,000
- INR: ₹18,75,000 to ₹45,00,000
- Immunoglobulin Therapy (per month):
- USD: $1,000 to $5,000
- INR: ₹75,000 to ₹3,75,000
- Hospital Stay (for Bone Marrow Transplant or Gene Therapy):
- USD: $5,000 to $15,000
Frequently Asked Questions
SCID, often referred to as “bubble boy disease,” is a rare genetic disorder that severely impairs the immune system. Individuals with SCID lack functional T and B cells, making them highly susceptible to infections. Without proper treatment, even minor infections can become life-threatening.