Systemic Mastocytosis (SM) Treatment in India
Systemic Mastocytosis (SM) is a rare disorder characterized by the accumulation of mast cells in multiple organs throughout the body, including the bone marrow, skin, liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and gastrointestinal tract. Mast cells are a type of white blood cell involved in the body's immune response, particularly in allergic reactions. They release histamine and other chemicals that can cause inflammation and allergic symptoms. In systemic mastocytosis, these mast cells become abnormally numerous and overactive, leading to a variety of symptoms and potential organ damage.
Systemic Mastocytosis
Systemic Mastocytosis is a rare condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of mast cells in various body tissues. Mast cells are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system, particularly in allergic reactions. When these cells accumulate in excess, they can cause various health issues, ranging from skin problems to more severe systemic complications.
Causes of Systemic Mastocytosis
The exact cause of Systemic Mastocytosis is not well understood, but it is often associated with mutations in the KIT gene, which regulates the growth and development of mast cells. This mutation leads to the uncontrolled proliferation of these cells, causing symptoms and complications.
Types of Systemic Mastocytosis
Systemic Mastocytosis can be classified into several types based on the severity and distribution of mast cells:
- Indolent Systemic Mastocytosis (ISM): The most common form, with mild symptoms and slow progression.
- Smoldering Systemic Mastocytosis (SSM): A more severe form than ISM, with a higher risk of organ damage.
- Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis (ASM): A rare and severe form that can lead to significant organ dysfunction.
- Mast Cell Leukemia (MCL): The most severe and rare form, where mast cells rapidly proliferate and affect the blood.
- Mast Cell Sarcoma: An extremely rare and aggressive form of mast cell tumor.
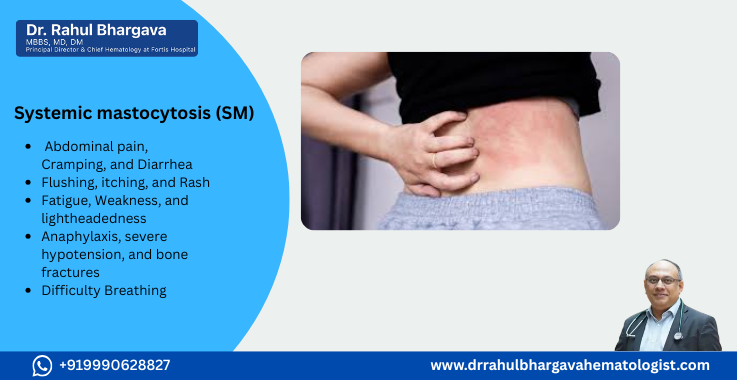
Symptoms of Systemic Mastocytosis
Symptoms of Systemic Mastocytosis can vary widely depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Skin rashes and itching
- Flushing or redness of the skin
- Abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea
- Anaphylaxis or severe allergic reactions
- Bone pain and osteoporosis
- Fatigue and weight loss
- Enlarged liver, spleen, or lymph nodes
Diagnosis of Systemic Mastocytosis
Diagnosing Systemic Mastocytosis typically involves a combination of the following tests:
- Blood Tests: To check for elevated levels of tryptase, a marker of mast cell activity.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: To assess the presence and number of mast cells in the bone marrow.
- Genetic Testing: To identify mutations in the KIT gene.
- Imaging Tests: Such as CT scans or MRI, to check for organ involvement.
Treatment Options for Systemic Mastocytosis
Treatment for Systemic Mastocytosis is tailored to the individual’s symptoms and the severity of the disease. Options include:
- Antihistamines: To manage allergic symptoms such as itching and flushing.
- Mast Cell Stabilizers: To prevent the release of mediators from mast cells.
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and manage severe symptoms.
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Targeted therapy for patients with KIT mutations.
- Chemotherapy: For aggressive forms like Mast Cell Leukemia.
- Bone Marrow Transplant: In select cases, particularly in aggressive or advanced forms of the disease.
Cost of Treatment and Stay in India
The cost of treating Systemic Mastocytosis in India is relatively affordable compared to many Western countries, making it an attractive option for medical tourism. The total cost of treatment, including hospital stay, can vary depending on the severity of the condition, the type of treatment required, and the duration of care. Here’s an overview of the costs:
-
Initial Consultation:
USD: $30 – $100
INR: ₹2,200 – ₹7,400 -
Blood Tests and Diagnostic Procedures:
USD: $50 – $200
INR: ₹3,700 – ₹14,800 -
Antihistamines and Mast Cell Stabilizers (monthly):
USD: $20 – $150
INR: ₹1,500 – ₹11,000 -
Corticosteroids and Targeted Therapy (monthly):
USD: $100 – $500
INR: ₹7,400 – ₹37,000 -
Chemotherapy (if required for severe cases):
USD: $1,000 – $5,000
INR: ₹75,000 – ₹3,70,000 -
Bone Marrow Transplant (if required):
USD: $15,000 – $25,000
INR: ₹12,00,000 – ₹20,00,000 -
Hospital Stay (per night):
USD: $30 – $200
INR: ₹2,200 – ₹15,000 per night
India’s healthcare system offers a range of treatment options at affordable prices, providing high-quality care while keeping costs lower than those in many Western nations. The overall treatment duration depends on the severity of Systemic Mastocytosis, with some cases requiring long-term management.
Frequently Asked Questions
The survival rate varies depending on the type and severity of the disease. Indolent forms have a good prognosis, while aggressive forms may have a more guarded outlook.
Currently, there is no cure for Systemic Mastocytosis, but treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Avoiding known triggers, such as certain foods, medications, or environmental factors that can provoke mast cell activation, is crucial. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing stress are also important in managing the condition.
Systemic Mastocytosis involves the accumulation of mast cells in multiple organs, such as the liver, spleen, and bone marrow, whereas Cutaneous Mastocytosis is limited to the skin. Systemic Mastocytosis typically presents with more severe symptoms and may require more intensive treatment.