Thrombocytopenia with absent radius (TAR) syndrome
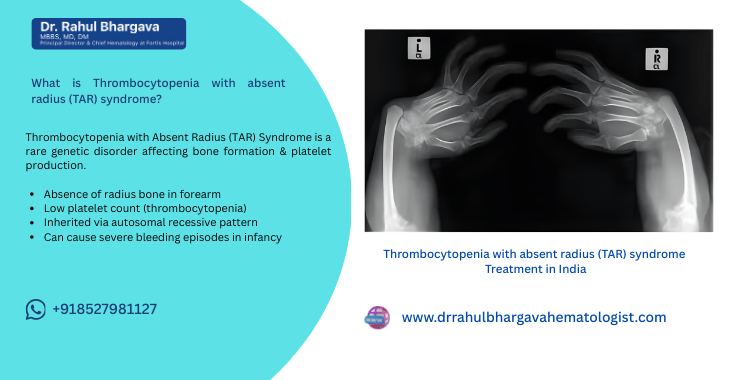
Thrombocytopenia with Absent Radius (TAR) syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the arms and blood cells. It is characterized by thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count) and absence of the radius bone in the forearm, which can lead to significant skeletal abnormalities. This condition is primarily inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning a person needs to inherit two copies of the defective gene (one from each parent) to develop the condition.
hrombocytopenia with Absent Radius (TAR) Syndrome
Thrombocytopenia with Absent Radius (TAR) Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the absence of the radius bone in the forearm and a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia). This condition can lead to severe bleeding issues in newborns and infants due to a lack of platelets. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Causes of TAR Syndrome
TAR Syndrome is a genetic disorder that occurs due to mutations in the RBM8A gene. The inheritance pattern of TAR Syndrome is autosomal recessive, meaning that both parents must carry the mutated gene for their child to develop the condition. Factors contributing to TAR include:
- Mutations in the RBM8A gene.
- Family history of the syndrome.
- Parental carriers of the mutated gene.
Types of TAR Syndrome
While TAR Syndrome does not have distinct “types” like some other conditions, it can vary in severity from patient to patient. The key factors influencing the severity include:
- Degree of thrombocytopenia: Platelet counts can fluctuate, affecting the risk of bleeding.
- Skeletal abnormalities: While the absence of the radius bone is characteristic, other skeletal abnormalities, such as leg or hip deformities, may also be present.
- Additional health concerns: Some individuals may have heart defects or gastrointestinal issues.
Understanding the range of severity helps in personalizing treatment approaches.
Symptoms of TAR Syndrome
The symptoms of TAR Syndrome are apparent at birth or shortly after. The most common symptoms include:
- Absence of the radius bone: The forearms appear shortened with a bent appearance.
- Low platelet count: This can cause frequent bruising, nosebleeds, or even internal bleeding.
- Bleeding episodes: Due to thrombocytopenia, newborns may experience life-threatening bleeding episodes.
- Other skeletal abnormalities: Some individuals may also experience leg, hip, or knee deformities.
- Heart or gastrointestinal issues: Some children with TAR Syndrome may have congenital heart defects or feeding problems.
Diagnosis of TAR Syndrome
The diagnosis of TAR Syndrome involves a combination of clinical evaluations, genetic testing, and imaging. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Physical Examination: A thorough check for the absence of the radius bone and other skeletal deformities.
- Platelet Count Test: To confirm thrombocytopenia, a blood test is conducted to assess the platelet levels.
- Genetic Testing: To identify mutations in the RBM8A gene.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays or other imaging to confirm the absence of the radius bone and evaluate additional skeletal abnormalities.
Treatment of TAR Syndrome
While there is no cure for TAR Syndrome, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. The treatment plan may include:
- Platelet transfusions: To address low platelet counts and prevent bleeding episodes, particularly in infancy.
- Surgery: Orthopedic surgeries to correct skeletal deformities or improve functionality.
- Medications: Certain medications may be prescribed to manage bleeding risks.
- Physical Therapy: Helps improve mobility and strengthen affected limbs.
- Specialized Care: Children with TAR Syndrome may need specialized care for associated conditions such as heart defects or gastrointestinal problems.
Cost of Treatment and Stay in India
The cost of treating Thrombocytopenia with Absent Radius (TAR) Syndrome in India is relatively affordable compared to many Western countries. The cost of treatment depends on various factors such as the severity of the condition, the required medical interventions, and the duration of care. Here’s an overview of the costs involved:
-
Initial Consultation:
USD: $30 – $100
INR: ₹2,200 – ₹7,400 -
Platelet Transfusions (per session):
USD: $100 – $500
INR: ₹7,400 – ₹37,000 -
Surgical Intervention (Orthopedic surgeries for skeletal deformities):
USD: $2,000 – $10,000
INR: ₹1,50,000 – ₹7,50,000 -
Medications (for bleeding management and other symptoms):
USD: $50 – $300 per month
INR: ₹3,700 – ₹22,200 per month -
Physical Therapy (per session):
USD: $20 – $60
INR: ₹1,500 – ₹4,400 per session -
Hospital Stay (per night):
USD: $25 – $200
INR: ₹2,000 – ₹15,000 per night
India offers comprehensive and affordable healthcare services, making it an attractive destination for the treatment of rare genetic conditions like TAR Syndrome. Costs are considerably lower than those in Western countries, while maintaining high-quality care and treatment options
Frequently Asked Questions
With proper medical care, individuals with TAR Syndrome can live full and active lives. Lifelong monitoring and treatment are necessary to manage platelet levels and any skeletal abnormalities.
There is no cure for TAR Syndrome, but its symptoms can be managed effectively with proper treatment and medical intervention.
Yes, TAR Syndrome can be detected during pregnancy through genetic testing and detailed ultrasound imaging, particularly if there is a family history of the condition.