Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS)
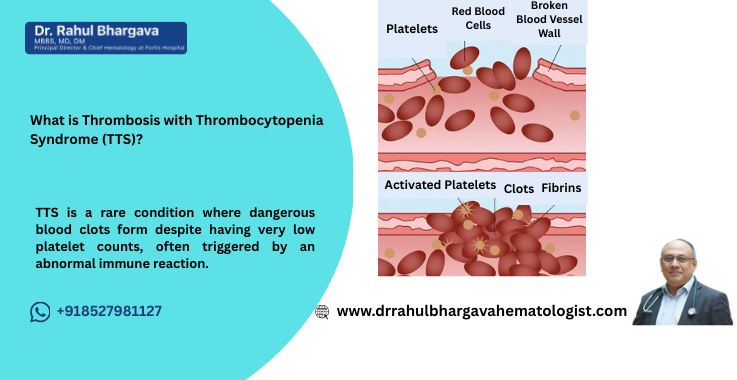
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS) is a rare and serious condition that involves the formation of blood clots (thrombosis) in unusual locations, along with a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia). TTS can lead to severe complications such as organ damage or stroke. The condition gained significant attention in 2021 due to its association with certain COVID-19 vaccines, particularly the AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson vaccines, although TTS can occur in other contexts as well.
TTS is distinct from other forms of thrombocytopenia, such as immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), due to its association with thrombosis. It involves a complex immune response that triggers the activation of platelets and clot formation while simultaneously lowering the number of circulating platelets, creating a dangerous paradox.
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS)
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS) is a rare but serious condition that occurs when blood clots (thrombosis) form in veins or arteries, combined with low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia). TTS has been linked to certain medications or vaccines, but the overall risk remains very low. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications, including stroke, pulmonary embolism, or other life-threatening conditions.
Causes of TTS
The exact causes of TTS are still under study. However, some potential factors include:
- COVID-19 Vaccines: Certain adenovirus-vector vaccines, like AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson, have been linked to rare cases of TTS.
- Medications: Some anticoagulant medications may trigger TTS in rare cases.
- Autoimmune Disorders: In some cases, TTS is thought to be an autoimmune response, where the body’s immune system attacks its platelets.
Types of TTS
There are two main types of TTS based on the location of blood clots:
- Venous Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia: Blood clots form in veins, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST).
- Arterial Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia: Blood clots form in arteries, which may lead to more serious events such as heart attacks or strokes.
Symptoms of TTS
Early recognition of TTS symptoms is crucial for effective treatment. Common signs include:
- Severe headaches or migraines (especially with vision changes or seizures)
- Swelling or pain in the limbs (indicating possible DVT)
- Chest pain, shortness of breath (could indicate pulmonary embolism)
- Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting
- Easy bruising or unexplained bleeding
- Fatigue and weakness
Diagnosis of TTS
Dr. Rahul Bhargava uses a comprehensive diagnostic approach to confirm TTS. Common diagnostic tests include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): To check platelet levels and blood cell count.
- D-Dimer Test: To measure clot formation.
- Imaging Tests: CT or MRI scans may be used to identify blood clots in the brain or other areas.
- Blood Clotting Studies: To analyze how quickly your blood clots.
Early diagnosis and intervention are key to managing TTS effectively.
Treatment for TTS
The treatment plan for TTS focuses on stopping clot formation and improving platelet counts. Dr. Bhargava tailors the treatment based on the severity of each case:
- Anticoagulant Therapy: Medications like non-heparin anticoagulants are used to prevent further clot formation.
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG): Used to help raise platelet levels.
- Corticosteroids: To reduce the immune response and prevent further damage to platelets.
- Plasma Exchange: In severe cases, plasma exchange may be required to remove harmful antibodies from the blood.
Cost of Treatment and Stay in India
The cost of treating Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS) in India is relatively affordable compared to Western countries. The total cost of treatment, including hospital stay, can vary depending on the severity of the condition, the type of treatment required, and the healthcare facility. Here’s an overview of the costs:
-
Initial Consultation:
USD: $30 – $100
INR: ₹2,200 – ₹7,400 -
Diagnostic Tests (CBC, D-Dimer, Imaging Tests, Blood Clotting Studies):
USD: $50 – $200
INR: ₹3,700 – ₹14,800 -
Anticoagulant Therapy (per month):
USD: $100 – $500
INR: ₹7,400 – ₹37,000 -
Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) Therapy:
USD: $1,000 – $5,000
INR: ₹74,000 – ₹3,70,000 -
Corticosteroids (per month):
USD: $50 – $200
INR: ₹3,700 – ₹14,800 -
Plasma Exchange (per session):
USD: $1,500 – $3,000
INR: ₹1,10,000 – ₹2,20,000 -
Hospital Stay (per night):
USD: $50 – $200
INR: ₹3,700 – ₹14,800
India offers cost-effective healthcare services, making it a popular destination for the treatment of rare conditions like TTS. The costs are significantly lower than in Western countries, while still ensuring high standards of medical care and advanced treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of TTS and the treatment plan. Most patients recover within a few weeks, but close follow-up is required to monitor progress.
While TTS is rare, maintaining overall health, staying hydrated, and following vaccination guidelines can reduce the risk. Those with a history of clotting issues should consult their doctor before taking certain medications.
TTS can be life-threatening if not treated promptly, as it involves blood clots that can cause stroke or heart attack. Early diagnosis and treatment, however, significantly improve outcomes.